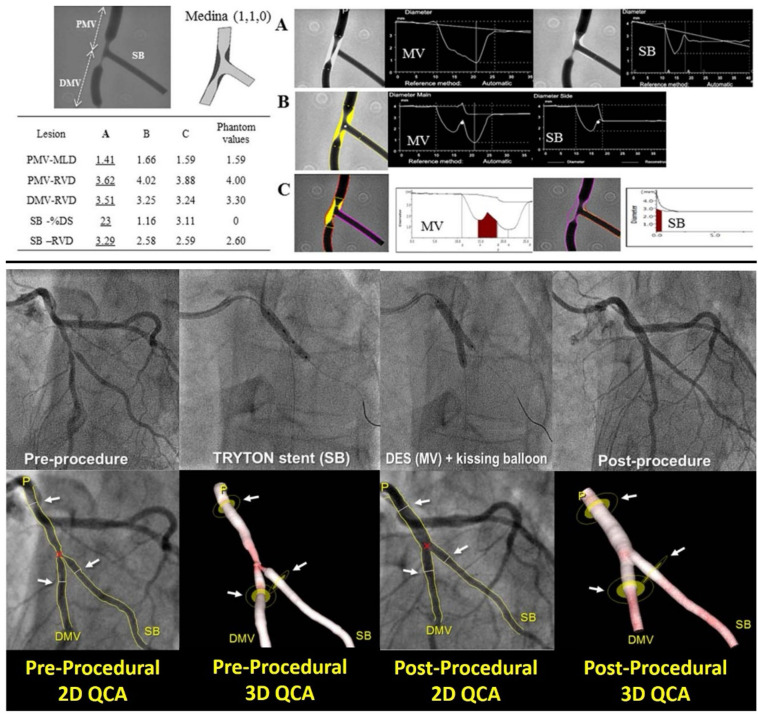
Figure 3.
Comparison of different software algorithms for coronary bifurcation analysis using calibrated phantoms (upper panel) and comparison between 2D and 3D quantitative coronary angiography bifurcation analyses (lower panel). Upper panel: This is an example of a case of the phantom model results. Quantitative coronary angiography measurement by CAAS and QAngio XA with automatic selection of the Y- or T-shape algorithm is shown for a bifurcated lesion in the calibrated phantom. Angiographic parameters including RVD, minimal lumen diameter, % diameter stenosis are given in the PMV, DMV, and SB. Case 1: A cine-angiogram demonstrated moderate to severe stenosis both in the PMV and the DMV in the Medina class (1,1,0) bifurcation. The conventional single-vessel method measured a significantly smaller RVD in the PMV and a larger RVD in the DMV and SB. (A) QCA is shown using the conventional single-vessel algorithm by CAAS. (B) QCA is shown using the bifurcation algorithm by CAAS. (C) QCA is shown using the bifurcation algorithm by QAngio XA with automatic selection of Y or T shape [Reproduced from Ishibashi et al. (41)]. Lower panel: Treatment procedure using the Tryton stent and the definition of the treated segment. A bifurcation lesion was observed in the mid segment of left anterior descending artery and a diagonal branch [left in (A)]. After pre-dilatation, a Tryton stent was implanted toward the side branch (center left), then a drug-eluting stent was implanted through the Tryton stent in the main vessel (center right). The final angiogram showed good results (right). The treated segments were delineated using three white lines (see white arrows) at the proximal main branch (PMB), distal main branch (DMB), and SB in the matched projections [white arrows, pre-procedure in (B) and post-procedure in panel (C)]. Specifically, the proximal and distal borders of the main vessel were set at the proximal and distal edge of the DES implanted, respectively. In this case, the distal border of side branch was defined as the distal edge of the Tryton stent [Reproduced from Muramatsu et al. (42)].