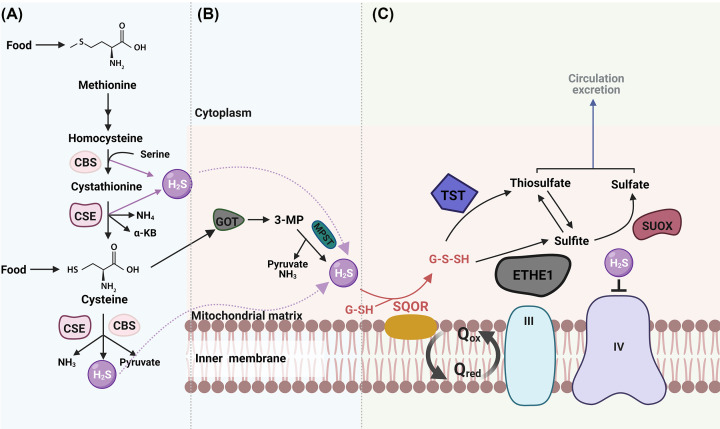
Figure 1. Schematic overview of the biosynthesis and disposal routes of hydrogen sulfide (H2S).
(A) Transsulfuration pathway in cytoplasm generated by the PLP-dependent enzymes: CBS and CSE. Methionine and cysteine are the main substrates of CBS and CSE, with the production of some intermediates such as serine, NH4, NH3 and pyruvate. Diet is the sole source of methionine. (B) Alternative enzymatic generation of H2S, mediated by GOT and MPST, mainly occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. (C) The oxidation pathway of H2S facilitated by the suite of mitochondrial enzymes. The disposal starts with the generation of G-SSH by SQOR, followed by further action by either TST or ETHE1 combined with SUOX to produce thiosulfate and sulfate, which are eventually excreted. 3-MP, 3-mercaptopyruvate; CBS, cystathionine β synthase; CSE, cystathionine γ lyase; ETHE1, ethylmalonic encephalopathy 1; GOT, glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase; MPST, mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase; PLP, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate; SUOX, sulfite oxidase; III, IV, complex III & IV in respiratory chain; SQOR, sulfide quinone oxidoreductase; TST, thiosulfate sulfur transferase; Qox, Oxidised coenzyme Q; Qred, Reduced coenzyme Q. (Created with BioRender.com.)