Abstract
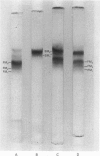
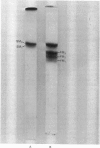
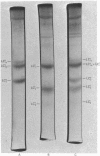
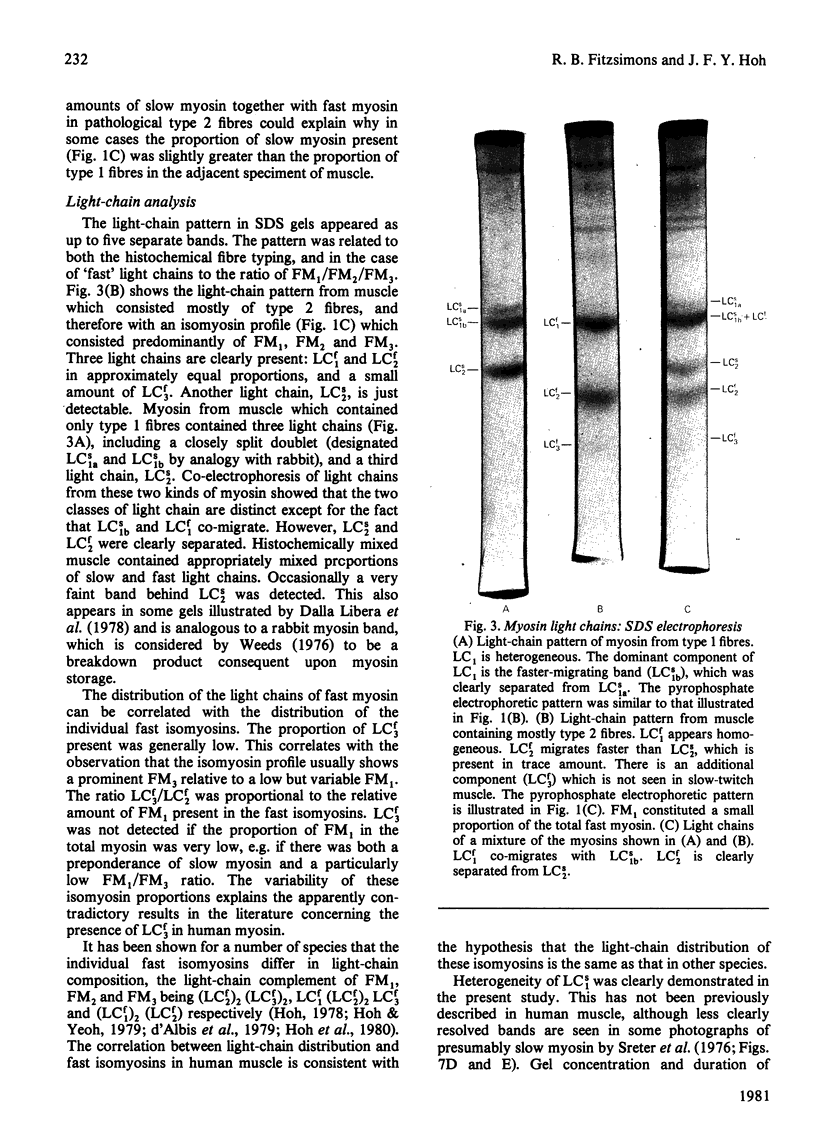
Human myosin from different skeletal muscles was analysed in a non-denaturing gel system, and the isoenzyme composition correlated with the histochemical composition of the muscle. Two components (SM1 and SM2) were associated with type 1 (slow-twitch) fibres, and three (FM1, FM2 and FM3) with type 2 (fast-twitch) fibres. Light-chain analysis was performed in sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gels. There are three light chains (LCs1a, LCS1b and LCs2) in type 1 fibres, and three (LCf1, LCf2 and LCf3) in type 2 fibres. LCf1 and LCs1b co-migrate in sodium dodecyl sulphate gels. The ratio of LCf3/LCf2 is correlated with the distribution of the individual fast isoenzymes. These results explain apparent discrepancies in the literature concerning the light-chain distribution of human myosin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailin G. Myosin and actomyosin from human skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 9;449(2):310–326. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H. Percutaneous needle-biopsy of skeletal muscle in diagnosis and research. Lancet. 1971 Sep 11;2(7724):593–595. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröschel-Stewart U. Comparative studies of human smooth and striated muscle myosins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 16;229(2):322–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90191-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L., Samaha F. J. Qualitative differences between actomyosin ATPase of slow and fast mammalian muscle. Exp Neurol. 1969 Sep;25(1):138–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F. Light chain distribution of chicken skeletal muscle myosin isoenzymes. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 15;90(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F., Yeoh G. P. Rabbit skeletal myosin isoenzymes from fetal, fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):321–323. doi: 10.1038/280321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. Y., McGrath P. A., White R. I. Electrophoretic analysis of multiple forms of myosin in fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles of the chick. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):87–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1570087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. A., Polgar J., Weightman D., Appleton D. Data on the distribution of fibre types in thirty-six human muscles. An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Jan;18(1):111–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libera L. D., Margreth A., Mussini I., Cerri C., Scarlato G. Myosin polymorphism in human skeletal muscles. Muscle Nerve. 1978 Jul-Aug;1(4):280–291. doi: 10.1002/mus.880010404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Benefield P. A., Silberstein L., Lang L. M. Distribution of light chains in fast skeletal myosin. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):522–524. doi: 10.1038/282522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Risby D. Light chains from fast and slow muscle myosins. Nature. 1971 Nov 12;234(5324):81–85. doi: 10.1038/234081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A., HERMAN E. Factors affecting the activity of adenosine triphosphatase and other phosphatases as measured by histochemical techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 May;3(3):161–169. doi: 10.1177/3.3.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn A. S., Cloak R. A., Rowland L. P. Myosin from normal and dystrophic human muscle. Immunochemical and electrophoretic studies. Arch Neurol. 1972 Aug;27(2):159–173. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490140063010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette D., Henriksson J., Emmerich M. Myofibrillar protein patterns of single fibres from human muscle. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 1;103(1):152–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette D., Schnez U. Coexistence of fast and slow type myosin light chains in single muscle fibres during transformation as induced by long term stimulation. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):128–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80656-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaha F. J. Actomyosin alterations in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jun;28(6):405–407. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490240065011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaha F. J., Thies W. H. Myosin light chains in Duchenne dystrophy and paraplegic muscle. Neurology. 1979 Jan;29(1):122–125. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Sreter F. A., Gergely J. Light chains of myosins from white, red, and cardiac muscles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):946–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streter F. A., Gergely J., Salmons S., Romanul F. Synthesis by fast muscle of myosin light chains characteristic of slow muscle in response to long-term stimulation. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 3;241(105):17–19. doi: 10.1038/newbio241017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G. Light chains from slow-twitch muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):157–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Lowey S. Substructure of the myosin molecule. II. The light chains of myosin. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 14;61(3):701–725. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Identification of a novel form of myosin light chain present in embryonic muscle tissue and cultured muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Albis A., Pantaloni C., Bechet J. J. An electrophoretic study of native myosin isozymes and of their subunit content. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):261–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]