Abstract
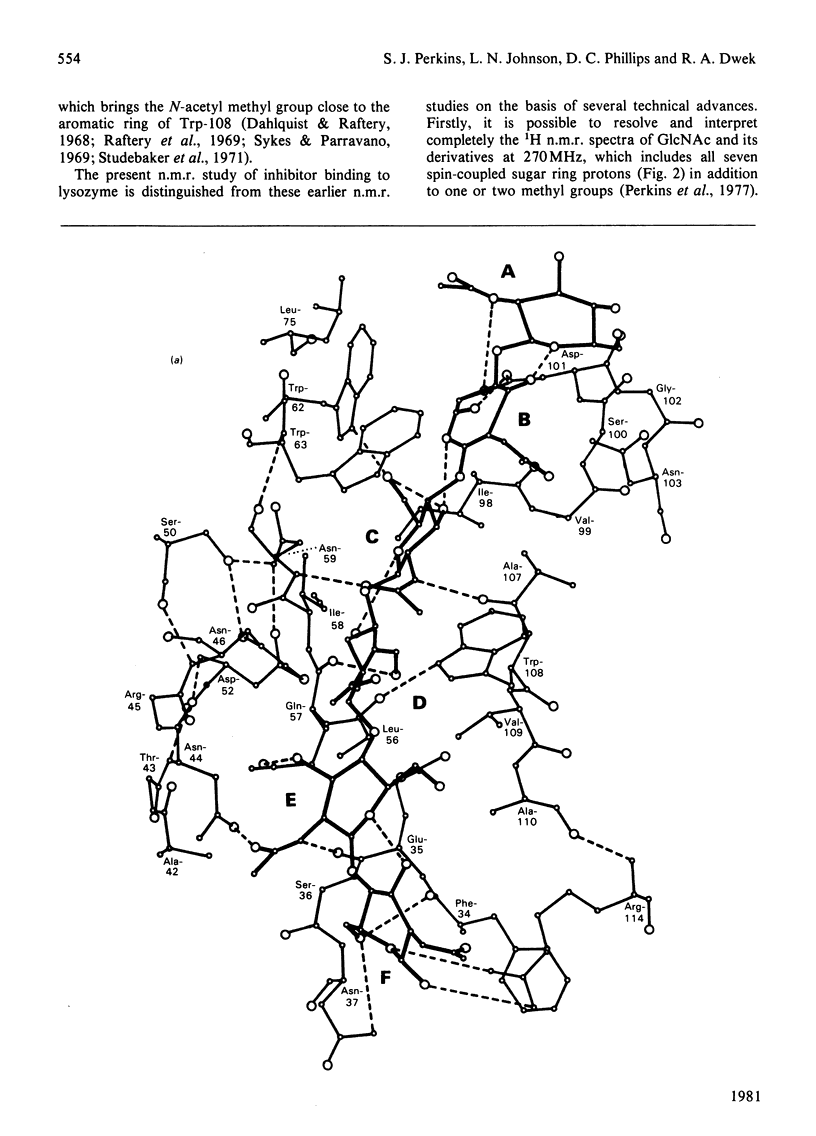
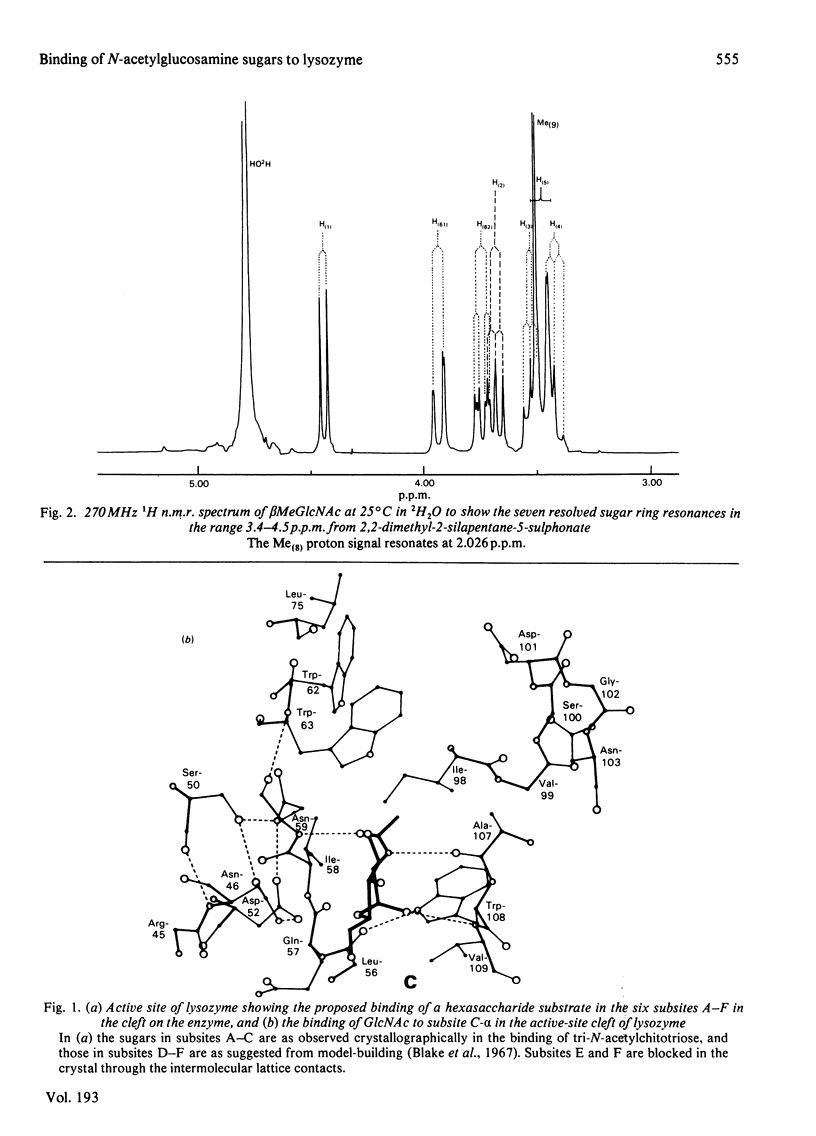
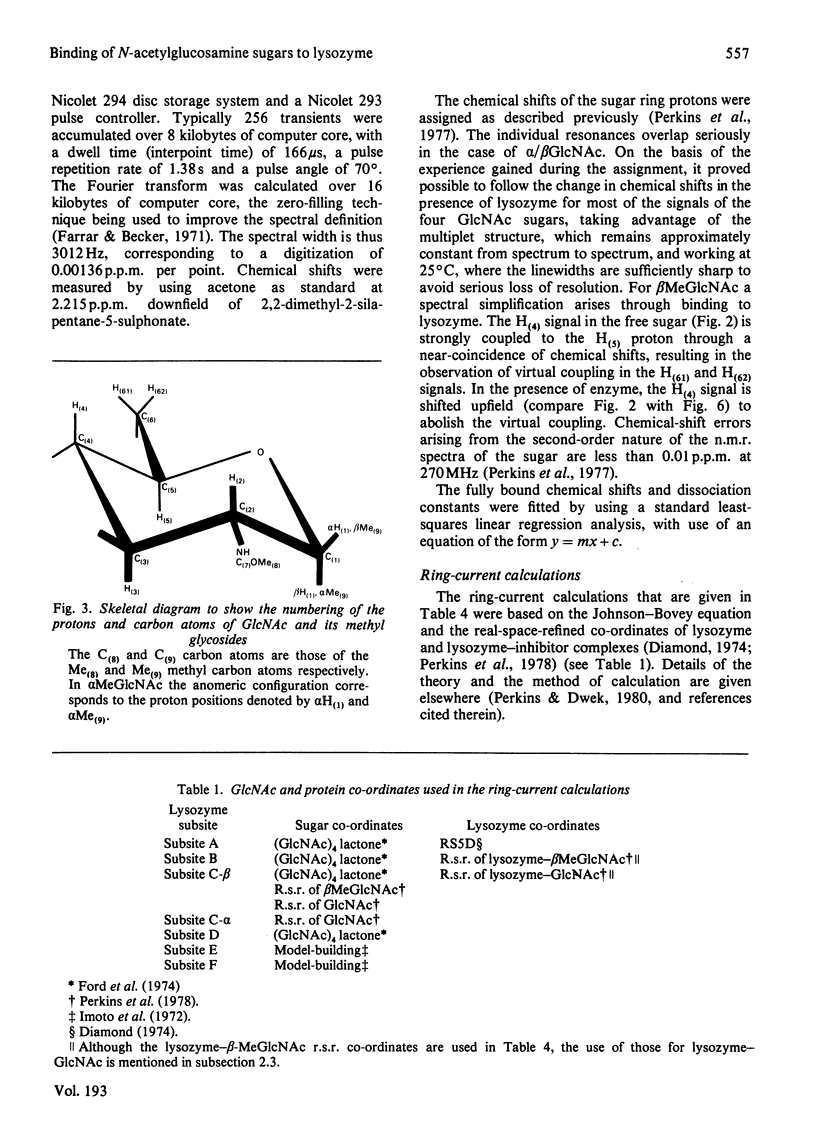
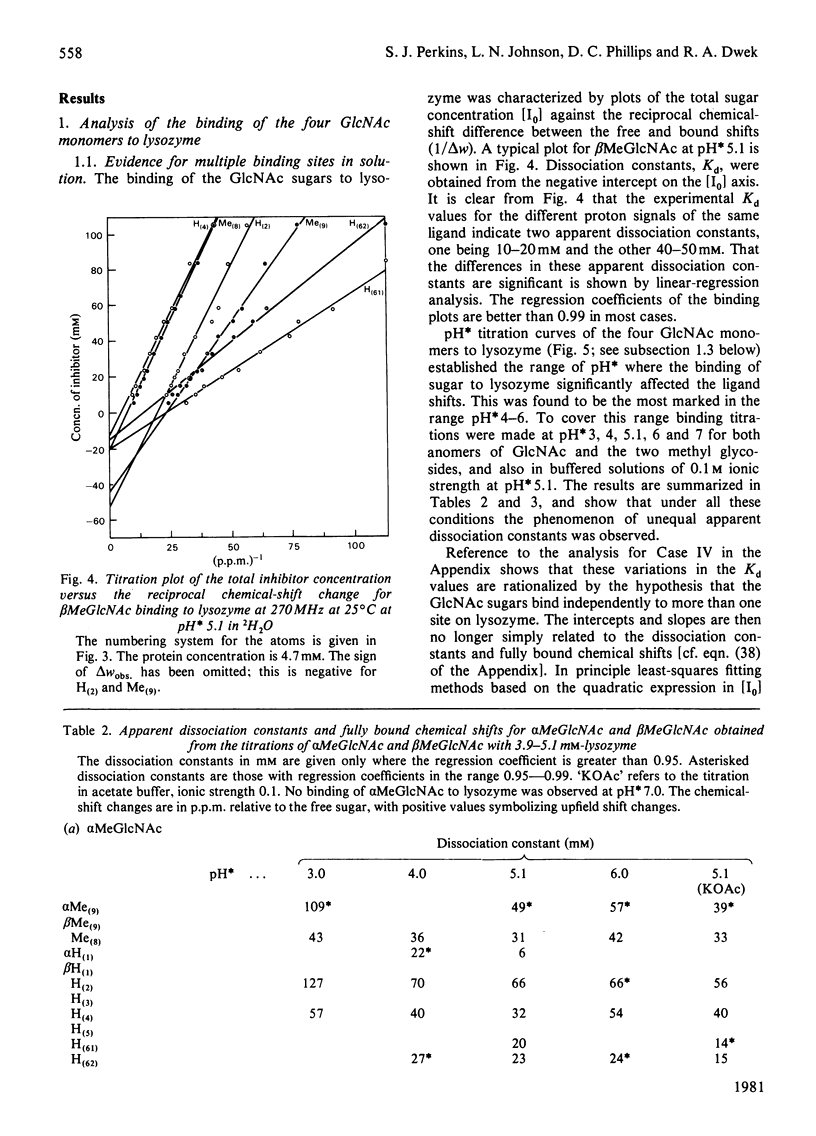
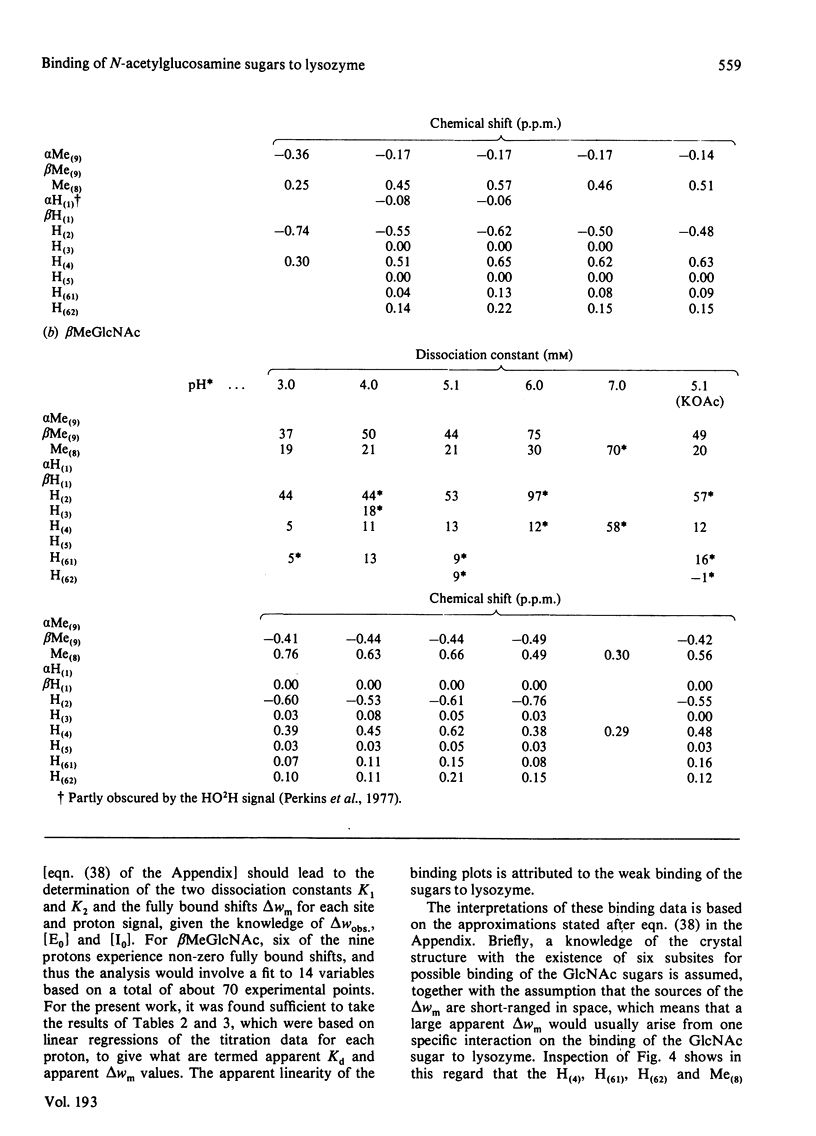
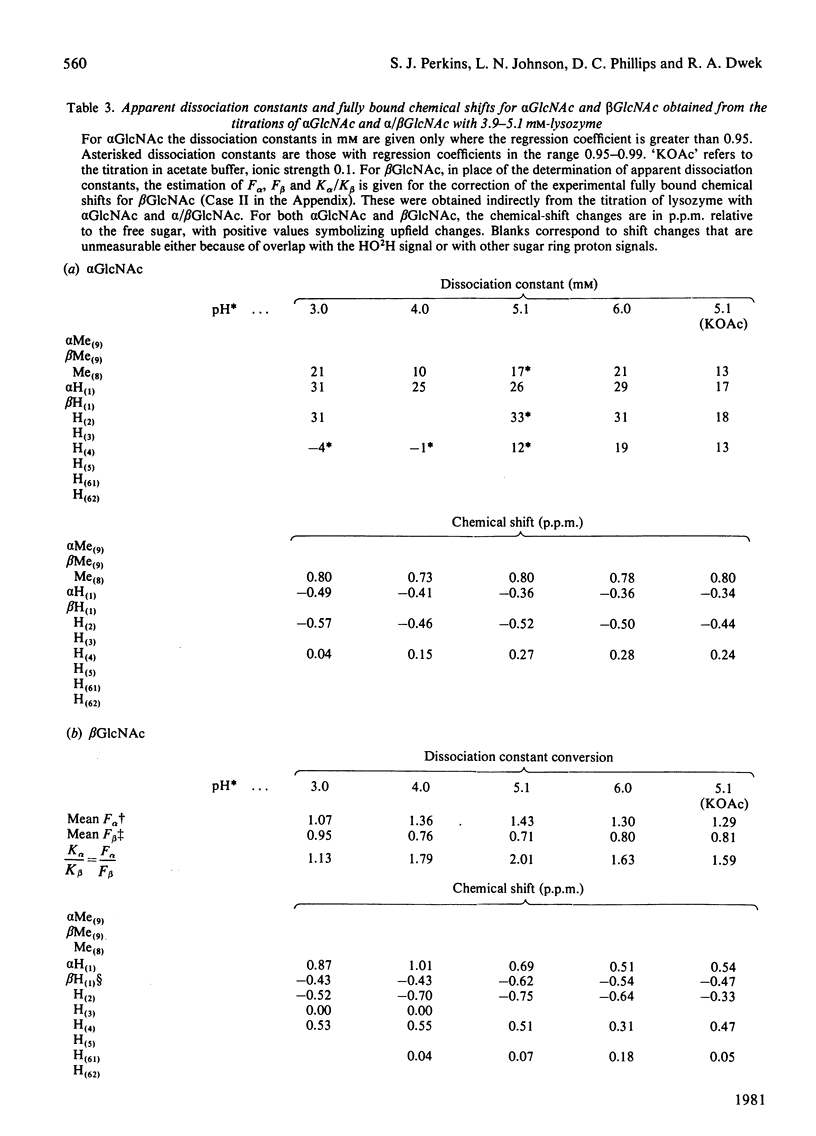
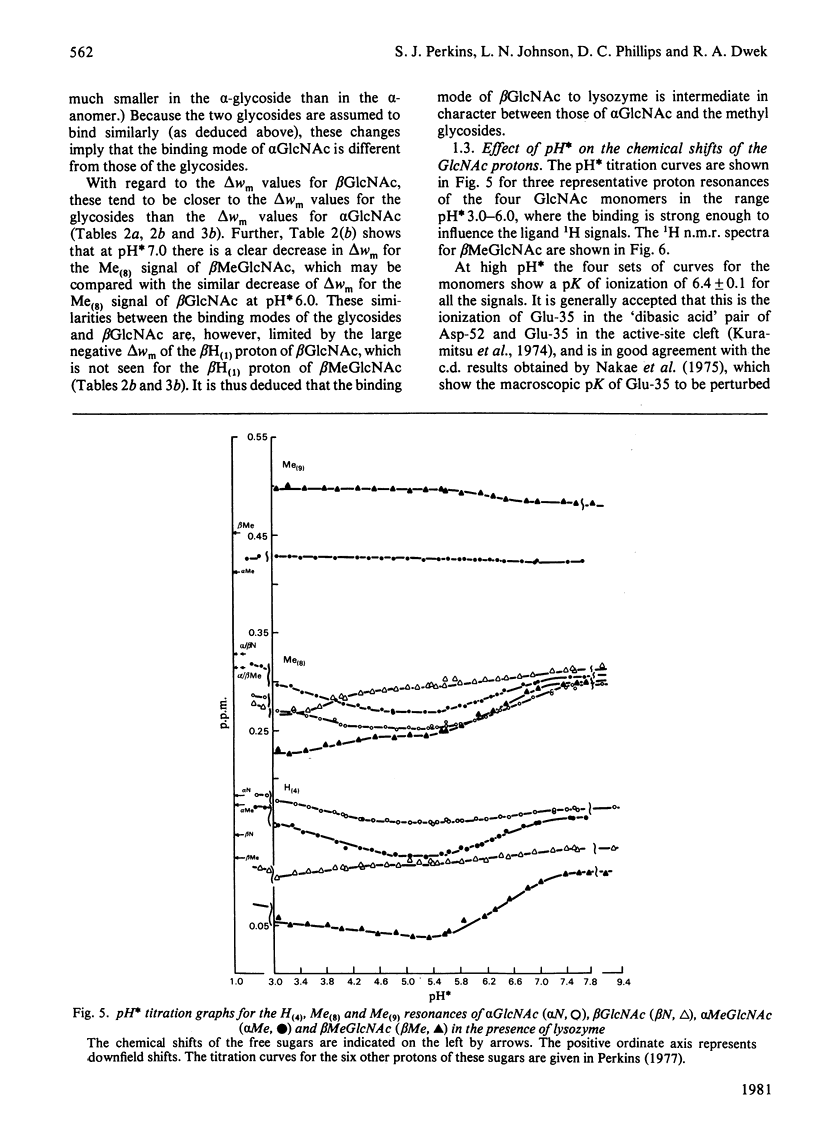
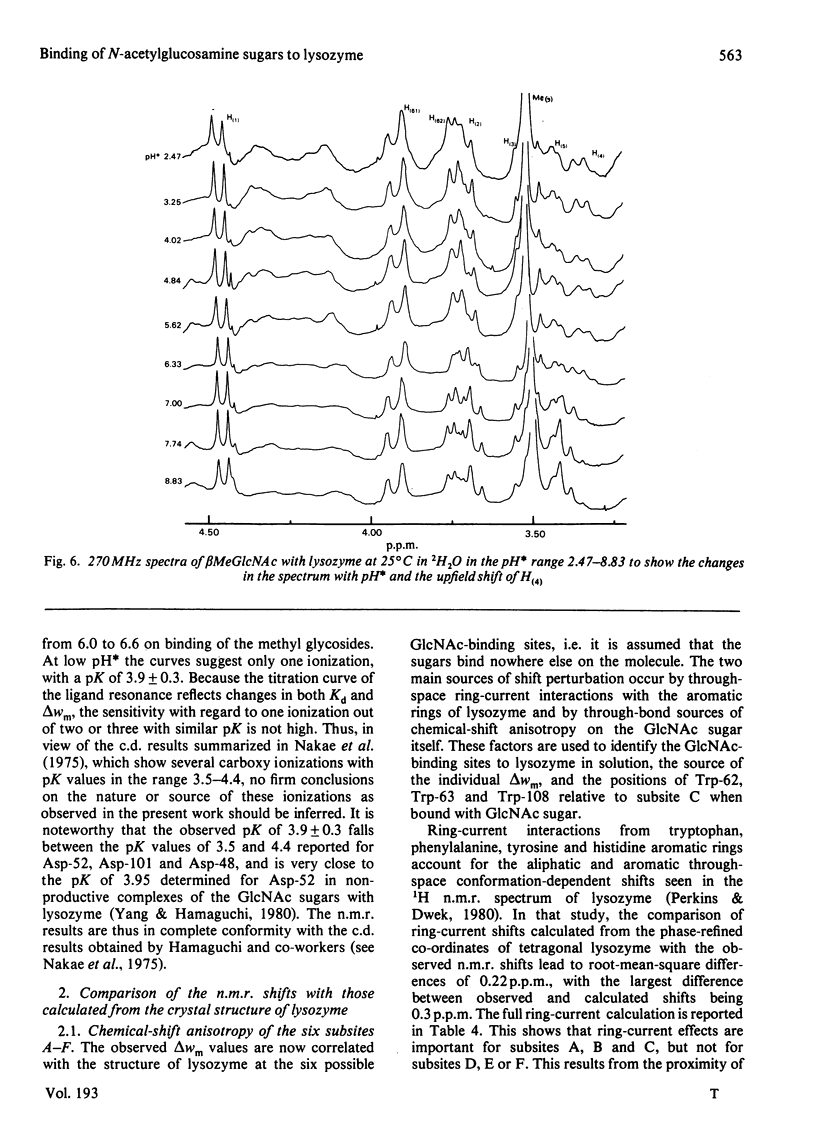
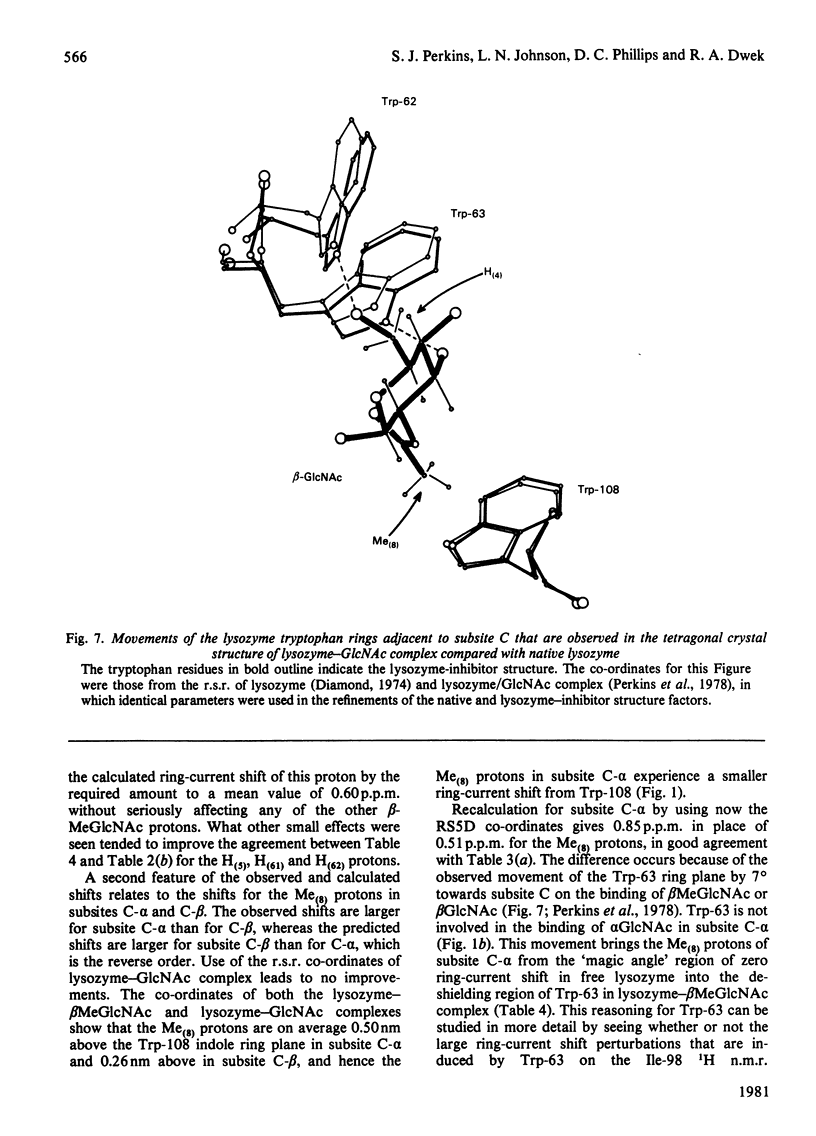
Studies of the binding of the four sugars alpha- and beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) and its alpha- and beta-methyl glycosides to hen egg-white lysozyme (EC 3.2.1.17) by means of high-resolution 1H n.m.r. at 270 MHz are reported. The details of the binding analyses are described in an Appendix. The results show that the sugars bind independently to more than one site in lysozyme. The apparent fully bound chemical shifts to the inhibitor proton signals show that, although the major binding modes are generally similar for the four sugars, the binding of alpha GlcNAc is distinct from that of alpha MeGlcNAc and beta MeClcNAc. The binding of beta GlcNAc is intermediate in character between these two modes. The observed shift changes of the inhibitor signals are correlated with the crystal structures of lysozyme-inhibitor complexes by the use of Johnson-Bovey ring-current calculations. Together with consideration of the chemical-shift anisotropy of the GlcNAc amide group, these suggest that GlcNAc-binding sites in solution are in subsites C and E. The calculations show also that the indole rings of Trp-62 and Trp-63 rotate towards subsite C on the binding of GlcNAc, whereas Trp-108 moves away slightly. These findings indicate a difference between the solution and tetragonal crystal forms of lysozyme-GlcNAc and lysozymes-beta MeGlcNAc complexes. In the crystal structure, binding of acetamido monosaccharides is only observed in subsite C, and binding in subsite E is prevented by crystal packing.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artymiuk P. J., Blake C. C., Grace D. E., Oatley S. J., Phillips D. C., Sternberg M. J. Crystallographic studies of the dynamic properties of lysozyme. Nature. 1979 Aug 16;280(5723):563–568. doi: 10.1038/280563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldo J. H., Halford S. E., Patt S. L., Sykes B. D. The stepwise binding of small molecules to proteins. Nuclear magnetic resonance and temperature jump studies of the binding of 4-(N-acetylaminoglucosyl)-N-acetylglucosamine to lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1975 May 6;14(9):1893–1899. doi: 10.1021/bi00680a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beddell C. R., Moult J., Phillips D. C. Crystallographic studies of the active site of lysozyme. In: Molecular properties of drug receptors. Ciba Found Symp. 1970:85–112. doi: 10.1002/9780470719763.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Grace D. E., Johnson L. N., Perkins S. J., Phillips D. C., Cassels R., Dobson C. M., Poulsen F. M., Williams R. J. Physical and chemical properties of lysozyme. Ciba Found Symp. 1977;(60):137–185. doi: 10.1002/9780470720424.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Johnson L. N., Mair G. A., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Sarma V. R. Crystallographic studies of the activity of hen egg-white lysozyme. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Apr 18;167(1009):378–388. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Koenig D. F., Mair G. A., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Sarma V. R. Structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. A three-dimensional Fourier synthesis at 2 Angstrom resolution. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):757–761. doi: 10.1038/206757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipman D. M., Grisaro V., Sharon N. The binding of oligosaccharides containing N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid to lysozyme. The specificity of binding subsites. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4388–4394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist F. W., Raftery M. A. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of association equilibria and enzyme-boud environments of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine anomers and lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3269–3276. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. Real-space refinement of the structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 25;82(3):371–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90598-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. O., Johnson L. N., Machin P. A., Phillips D. C., Tjian R. Crystal structure of a lysozyme-tetrasaccharide lactone complex. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):349–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90487-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Hamaguchi K. Binding of substrate analogues to subsites D, E, and F of hen egg-white lysozyme. J Biochem. 1976 Feb;79(2):237–247. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Hamaguchi K. State of Trp 62 in hen egg-white lysozyme bound with N-acetylchitooligosaccharides. J Biochem. 1975 Jan 1;77(1?):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. N., Phillips D. C., Rupley J. A. The activity of lysozyme: an interim review of crystallographic and chemical evidence. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1968 Jun;21(1):120–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Dwek R. A. The mechanism of water-proton relaxation in enzyme paramagnetic-ion complexes. 1. The Gd(3)-lysozyme complex. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):271–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu S., Ikeda K., Hamaguchi K., Fujio H., Amano T. Ionization constants of Glu 35 and Asp 52 in hen, turkey, and human lysozymes. J Biochem. 1974 Oct;76(4):671–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae Y., Ryo E., Kuramitsu S., Ikeda K., Hamaguchi K. pH dependence of the binding constants of N-acetylglucosamine monomers to hen and turkey egg-white lysozymes. J Biochem. 1975 Sep;78(3):589–597. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Dwek R. A. Comparisons of ring-current shifts calculated from the crystal structure of egg white lysozyme of hen with the proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of lysozyme in solution. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 22;19(2):245–258. doi: 10.1021/bi00543a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Johnson L. N., Machin P. A., Phillips D. C. Crystal structures of egg-white lysozyme of hen in acetate-free medium and of lysozyme complexes with N-acetylglucosamine and beta-methyl N-acetylglucosaminide. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):607–616. doi: 10.1042/bj1730607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Dahlquist F. W., Parsons S. M., Wolcott R. G. The use of nuclear magnetic resonance to describe relative modes of binding to lysozyme of homologous inhibitors and related substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):44–51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma R., Bott R. Crystallographic study of turkey egg-white lysozyme and its complex with a disaccharide. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 5;113(3):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sophianopoulos A. J. Association sites of lysozyme in solution. I. The active site. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3188–3193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studebaker J. F., Sykes B. D., Wien R. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of lysozyme inhibition. Effects of dimerization and pH on saccharide binding. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Sep 8;93(18):4579–4585. doi: 10.1021/ja00747a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. D. A transient nuclear magnetic resonance study of the kinetics of methyl N-acetyl-D-glucosaminide inhibition of lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):1110–1116. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. D., Parravano C. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of the inhibition of lysozyme by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and di-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 25;244(14):3900–3904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Hamaguchi K. Hydrolysis of 4-methylumbelliferyl N-acetyl-chitotrioside catalyzed by hen and turkey lysozymes. pH dependence of the kinetics constants. J Biochem. 1980 Apr;87(4):1003–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


