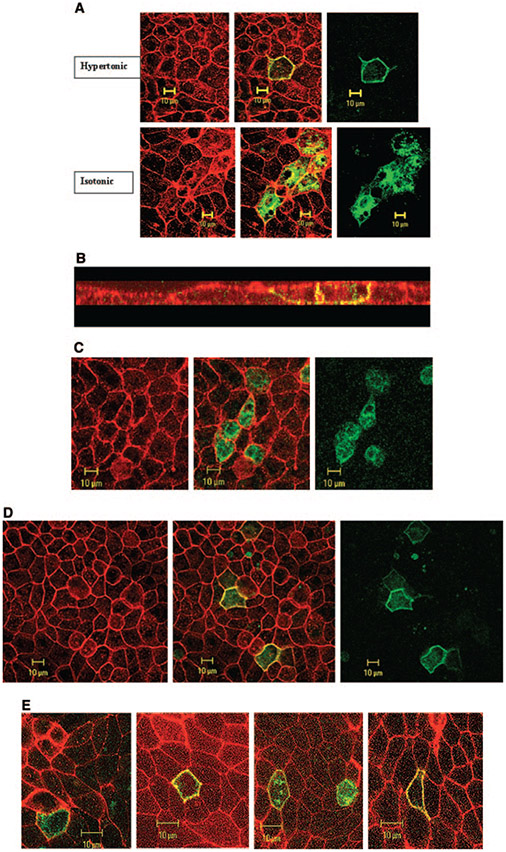
Figure 3.
Effect of hypertonicity on the expression and subcellular distribution of SLC26A7 in MDCK cells. (A) Expression of SLC26A7 in hypertonic medium (top) versus isotonic medium (bottom). As shown, SLC26A7 was detected almost exclusively in the plasma membrane in hypertonic medium (top) versus predominantly in intracellular compartments in isotonic medium (bottom). Red, phalloidin; green, SLC26A7-GFP. (B) Subcellular distribution studies in hypertonic medium. Merged Z-stack image of GFP-SLC26A7 and phalloidin indicates the targeting of SLC26A7 to the basolateral membrane. (C) Effect of 2 h of exposure to hypertonic medium on SLC26A7 distribution in MDCK cells. As shown, SLC26A7 was detected predominantly in the cytoplasm after 2 h of incubation in hypertonic medium. Red, phalloidin; green, SLC26A7-GFP. (D) Effect of mannitol on SLC26A7 distribution in MDCK cells. As shown, SLC26A7 was detected predominantly in the membrane after 16 h of incubation in hypertonic medium. Red, phalloidin; green, SLC26A7-GFP. (E) SLC26A7 expression in cells that were grown on permeable support. As shown, cells that were grown on permeable support were detected predominantly in the cytoplasm in isotonic medium. However, in cells that were exposed to hypertonic medium from the basolateral and apical surfaces or from the basolateral surface alone, SLC26A7 was detected predominantly on the plasma membrane. When hypertonicity was applied to the apical surface alone, SLC26A7 showed mild abundance in the membrane with significant retention in the cytoplasm.