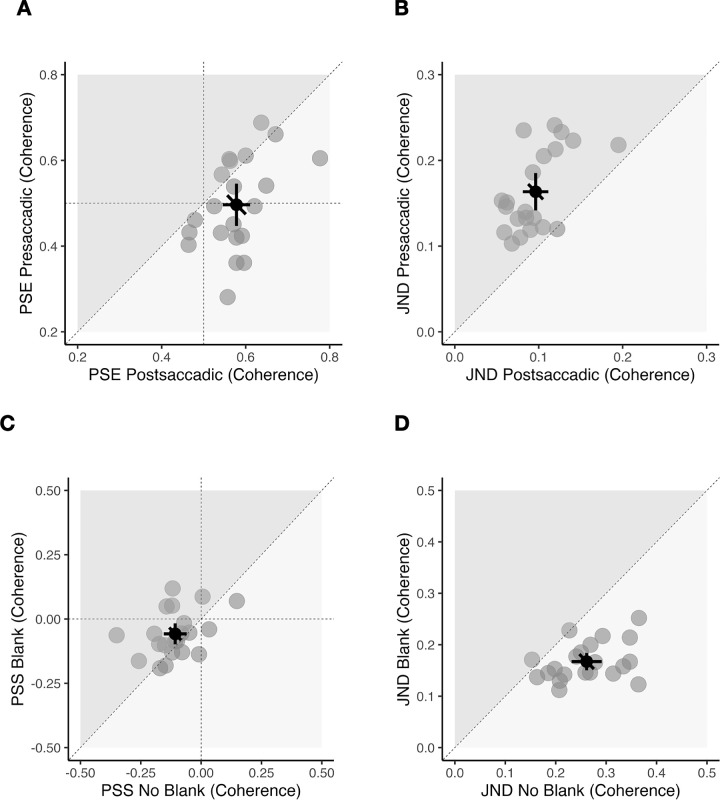
Figure 4.
Results of Experiment 1. (A and B) Appearance discrimination task. (C and D) Change discrimination task. (A) Scatterplot showing all points of subjective equality (PSE) compared between presaccadic (vertical axis) and postsaccadic (horizontal axis) conditions. Data points below the diagonal line indicate a less blurry appearance in the presaccadic compared to postsaccadic conditions. (B) Scatterplot for all just-noticeable differences (JNDs) compared between presaccadic (vertical axis) and postsaccadic (horizontal axis) conditions. Data points above the diagonal line indicate that participants were more precise in the postsaccadic condition. (C) Scatterplot showing all points of subjective stability (PSS) compared between blank (vertical axis) and no blank (horizontal axis) conditions. Data points in the lower left quadrant (negative PSS) indicate a bias toward blur-increase responses. (D) Scatterplot for all JNDs compared between blank (vertical axis) and no blank (horizontal axis) conditions. Data points below the diagonal line indicate higher precision in the blank condition. (A–D) Gray dots indicate individual participant data, black dot indicates the overall mean. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals.