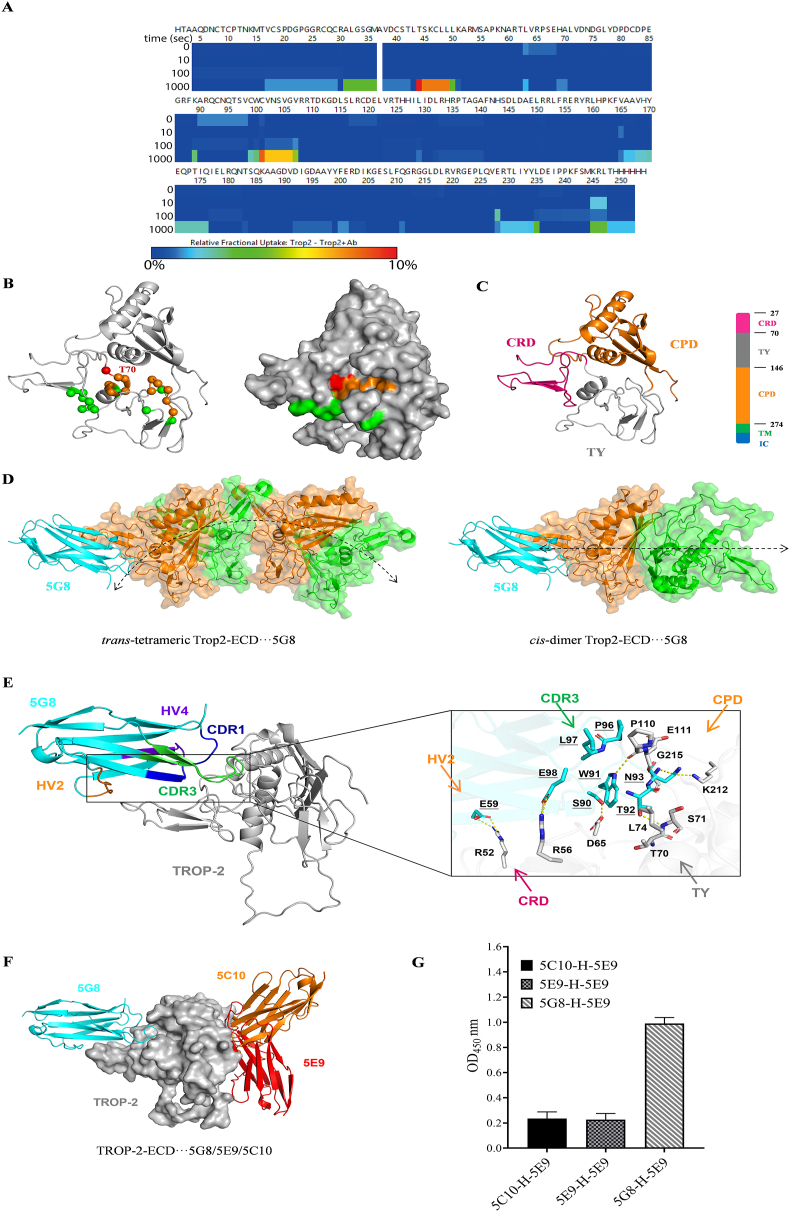
Figure 4.
HDX-MS and molecular dynamics simulation of TROP-2 in the presence of VNAR-5G8. (A) The heat map shows the difference in relative fractional uptake of deuterium between TROP-2 and TROP-2+5G8 by HDX-MS. (B) 3D projection of the regions with the most significant difference in relative fractional uptake of deuterium. The residues colored in red carried the largest difference (∼10%), the residues colored in brown carried the mild difference (∼5%), and the residues in green carried no difference (<1%). (C) Schematic diagram of TROP-2-ECD. TROP-2-ECD contains an ectodomain (27–274), consisting of a cysteine-rich domain (CRD), thyroglobulin type-1 domain (TY-1) and cysteine-poor domain (CPD), trans-membrane (TM), and cytoplasmic regions. The cartoon represents an ectodomain of TROP-2, including CRD (red), TY-1 domain (gray), and CPD (yellow), with all disulfide bonds shown as sticks. (D) Binding position of 5G8 on the trans-tetrameric and cis-dimer of TROP-2-ECD. The assembly direction of TROP-2-ECD is represented by a double-arrowed line. (E) Detailed view of TROP-2-ECD binding model with VNAR-5G8. VNAR-5G8 and TROP-2-ECD are represented as cyan, and grey cartoons. Key residues are indicated as cyan and grey rods. Hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dashed lines. Among them, HV4 of VNAR is purple, HV2 is orange, CDR3 is green, and CDR1 is blue. (F) Schematic representation of the structural overlay of the TROP-2-ECD···5G8, TROP-2-ECD···5E9, and TROP-2-ECD···5C10 composite systems. TROP-2-ECD, 5G8, 5E9, and 5C10 are denoted as grey surfaces, cyan, red and orange cartoons, respectively. (G) Double antibody sandwich ELISA was used to detect the epitope competition of VNAR binding to TROP-2 for the three shark VNARs. The horizontal and vertical axes represent the concentration and OD450 value of VNAR, respectively (mean ± SD, n = 3).