Abstract
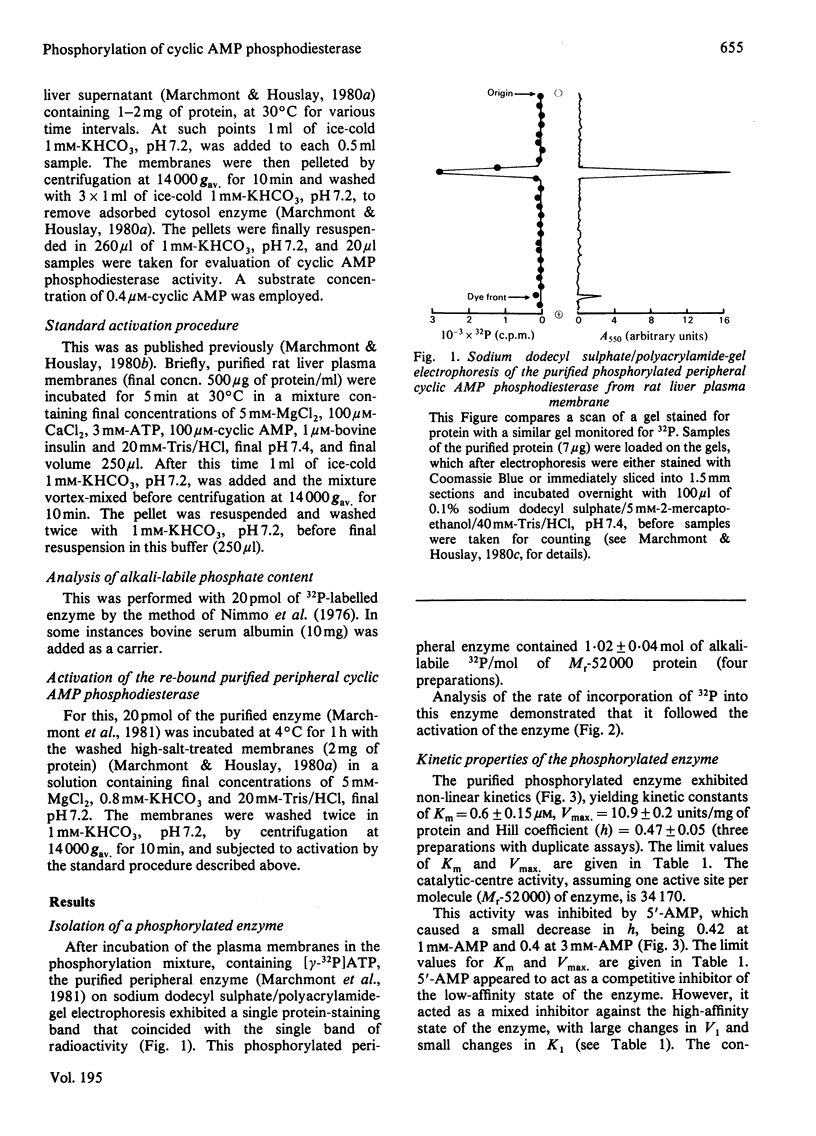
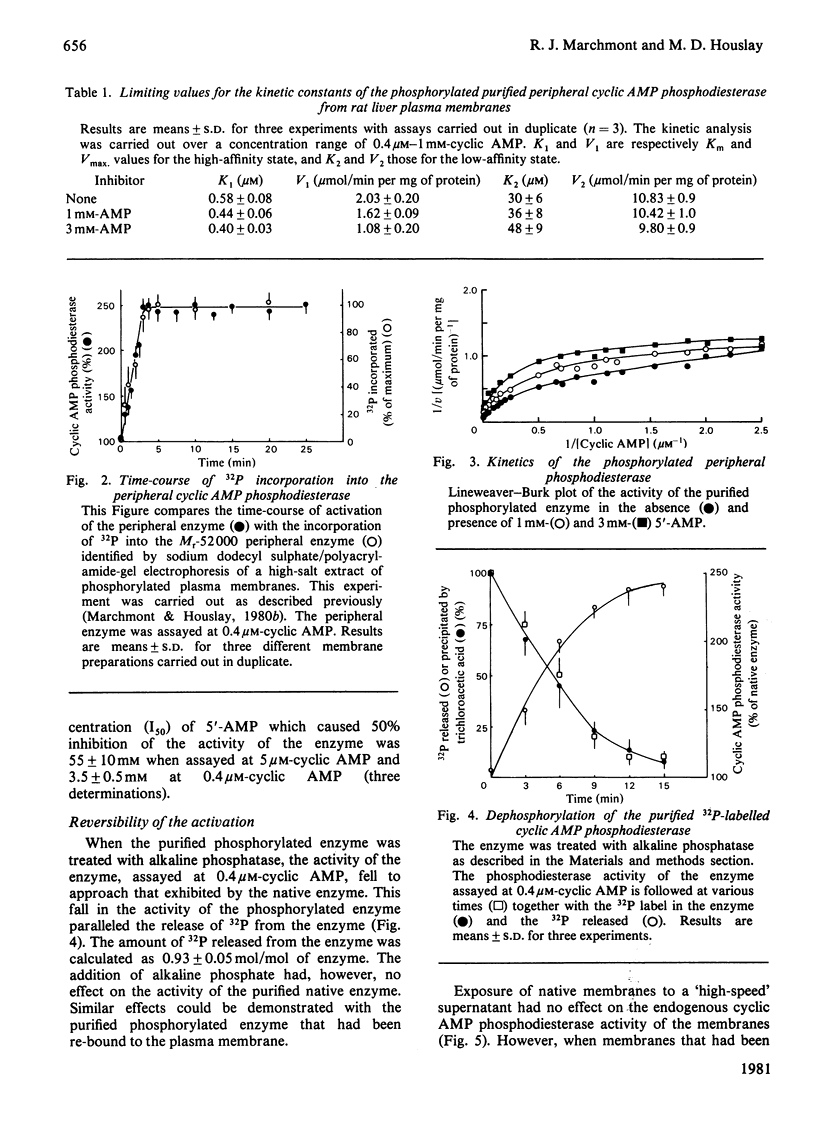
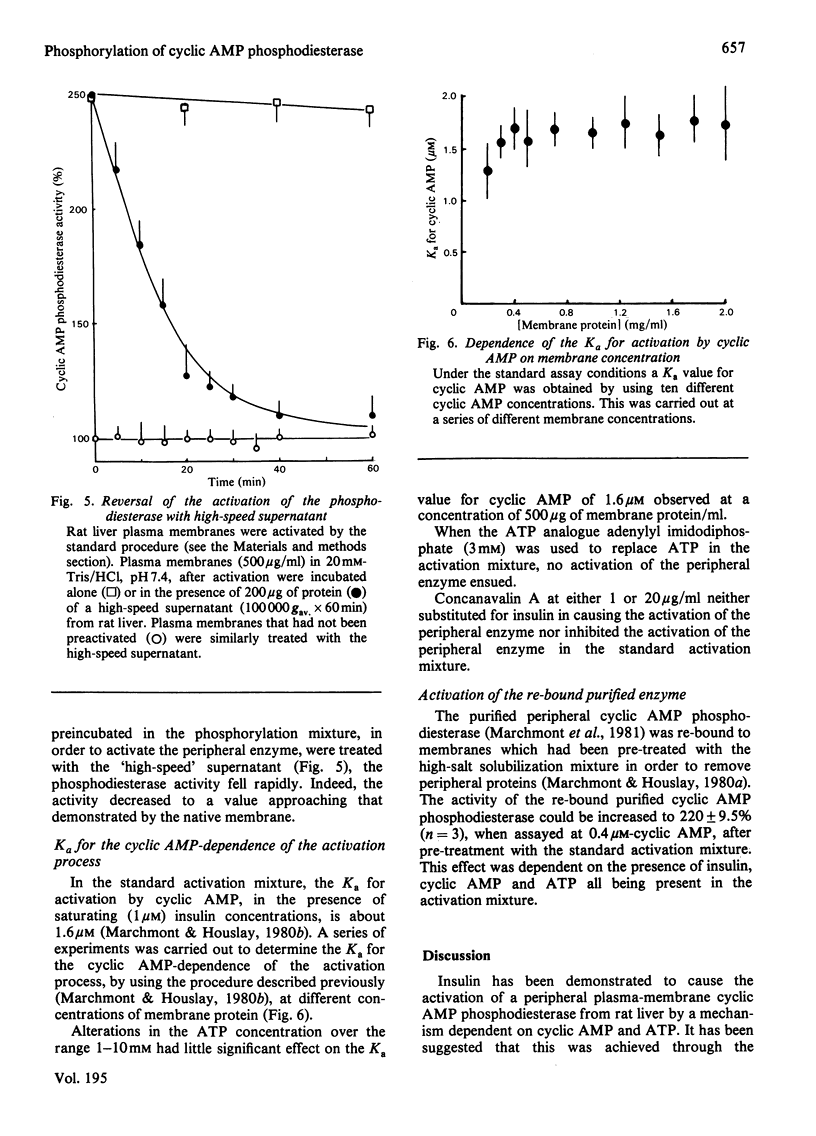
Incubation of intact purified rat liver plasma membranes with insulin, cyclic AMP and ATP led to the activation of the peripheral "low-Km" cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase. When (gamma-32P]ATP was included in the incubation mixture, after purification of this enzyme to homogeneity it was found to contain 1 mol of alkali-labile 32P/mol of enzyme. Treatment of the homogeneous phosphorylated enzyme with alkaline phosphatase released all of the 32P from the protein while restoring its activity to the native state. The reversibility of the activation that is achieved by the phosphorylation of this enzyme could also be demonstrated with a high-speed supernatant from rat liver. This restored the activity of the activated membrane-bound enzyme to its native state. The Ka for the cyclic AMP-dependence of this process (1.6 micrometer) was unaffected by a range of ATP concentrations (1-10 mM) and by a range of membrane protein concentrations (0.2-2 mg/ml). Adenylyl imidodiphosphate could not substitute for ATP, and concanavalin A could not substitute for insulin, as essential ligands in the activation process. The purified activated enzyme exhibited Km 0.6 microM, Vmax 10.9 units/mg of protein and Hill coefficient (h) 0.47. The Vmax. for this activated enzyme was much higher than that of the native enzyme, yet h was much lower.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball E. H., Seth P. K., Sanwal B. D. Regulatory mechanisms involved in the control of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterases in myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2962–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Chan T. M., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Insulin inhibition of alpha-adrenergic and glucagon actions in normal and calcium-depleted hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2828–2834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt H., Killilea S. D., Lee E. Y. Activation of phosphorylase phosphatase by a novel procedure: evidence for a regulatory mechanism involving the release of a catalytic subunit from enxyme-inhibitor complex(es) of higher molecular weight. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 27;61(2):598–604. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90999-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Molecular basis of insulin action. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:359–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Harper S. C., Tucker A. L., Flagg J. L., Park C. R. Effects of adrenalectomy and glucocorticoid replacement on gluconeogenesis in perfused livers from diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 2;329(1):41–57. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg V., Boughter J. M., Carlisle S., Hill D. E. Evidence for two insulin receptor populations on human erythrocytes. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):279–281. doi: 10.1038/286279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House P. D., Poulis P., Weidemann M. J. Isolation of a plasma-membrane subfraction from rat liver containing an insulin-sensitive cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 21;24(3):429–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb19703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D. Membrane phosphorylation: a crucial role in the action of insulin, EGF, and pp60src? Biosci Rep. 1981 Jan;1(1):19–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01115146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Palmer R. W. Changes in the form of Arrhenius plots of the activity of glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase and other hamster liver plasma-membrane enzymes occurring on hibernation. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):909–919. doi: 10.1042/bj1740909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Seals J. R. Pyruvate dehydrogenase activation in adipocyte mitochondria by an insulin-generated mediator from muscle. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1407–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.505013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Seals J. R. Pyruvate dehydrogenase activation in adipocyte mitochondria by an insulin-generated mediator from muscle. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1407–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.505013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Exton J. H., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W., Park C. R. Role of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the effects of insulin and anti-insulin serum on liver metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1031–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Sarver J. A., Vega F. V., Pointer R. H. Actions of insulin in fat cells. Effects of low temperature, uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation, and respiratory inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2226–2233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loten E. G., Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F. D., Exton J. H., Park C. R. Stimulation of a low Km phosphodiesterase from liver by insulin and glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):746–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loten E. G., Francis S. H., Corbin J. D. Proteolytic solubilization and modification of hormone-sensitive cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7838–7844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino H., de Buschiazzo P. M., Pointer R. H., Jordan J. E., Kono T. Characterization of insulin-sensitive phosphodiesterase in fat cells. I. Effects of salts and oxidation-reduction agents. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7845–7849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchmont R. J., Ayad S. R., Houslay M. D. Purification and properties of the insulin-stimulated cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase from rat liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 1;195(3):645–652. doi: 10.1042/bj1950645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchmont R. J., Houslay M. D. A peripheral and an intrinsic enzyme constitute the cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase activity of rat liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):381–392. doi: 10.1042/bj1870381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchmont R. J., Houslay M. D. Insulin controls the cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of integral and peripheral proteins associated with the rat liver plasma membrane. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 25;118(1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchmont R. J., Houslay M. D. Insulin trigger, cyclic AMP-dependent activation and phosphorylation of a plasma membrane cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):904–906. doi: 10.1038/286904a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo H. G., Cohen P. Hormonal control of protein phosphorylation. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:145–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo H. G., Proud C. G., Cohen P. The purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle glycogen synthase. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Exton J. H., Johnson R. A., Park C. R. Effects of glucagon on cyclic AMP and carbohydrate metabolism in livers from diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):250–267. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S. Characterization and comparison of membrane-associated and cytosolic cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Studies on human erythrocyte protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12439–12449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Dousa T. P. Plasma membrane cyclic AMP-dependent protein phosphorylation system in L6 myoblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 2;509(3):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., Czech M. P. Evidence that insulin activates an intrinsic plasma membrane protease in generating a secondary chemical mediator. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6529–6531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Wang T. H., Wirch E., Wang J. H. Purification and properties of bovine brain calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5916–5923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J., Olefsky J. M. Role of intracellular energy in insulin's ability to activate 3-O-methylglucose transport by rat adipocytes. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2183–2190. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. A., Elliott K. R., Pogson C. I. Differential effects of tryptophan on glucose synthesis in rats and guinea pigs. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):817–825. doi: 10.1042/bj1760817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. A simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S., Van Cauter E., Dumont J. E. Protein kinase and cyclic 3',5'-AMP: significance of binding and activation constants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 17;364(2):250–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Appleman M. M. Multiple cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activities from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Little S. A., Williams R. H. Effect of insulin and growth hormone on rat liver cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Biochemistry. 1973 May 8;12(10):1889–1894. doi: 10.1021/bi00734a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tria E., Scapin S., Cocco C., Luly P. Insulin-sensitive adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate phosphodiesterase of hepatocyte plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 24;496(1):77–87. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. N., Hardman J. G. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:119–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwood S. A., Luzio J. P., Flockhart D. A., Siddle K. Investigation of the subcellular distribution of cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase in rat hepatocytes, using a rapid immunological procedure for the isolation of plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 3;583(4):454–466. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisher M. H., Evans W. H. Functional polarity of the rat hepatocyte surface membrane. Isolation and characterization of plasma-membrane subfractions from the blood-sinusoidal, bile-Canalicular and contiguous surfaces of the hepatocyte. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):375–388. doi: 10.1042/bj1460375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinman B., Hollenberg C. H. Effect of insulin and lipolytic agents on rat adipocyte low Km cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2182–2187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


