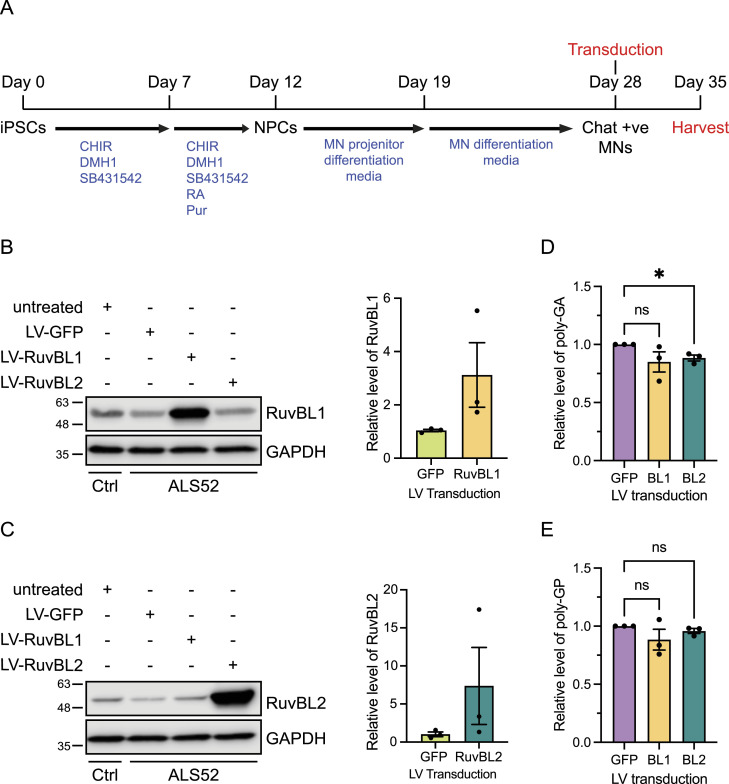
Figure 4. Lentiviral transduction with RuvBL2 reduces poly(GA) dipeptide repeats (DPRs) in C9orf72 patient iPSC-derived motor neurons.
(A) A timeline to illustrate the differentiation procedure of the iPSC motor neurons and the timepoint of transduction. iPSC-derived motor neurons from Control (Ctrl: CS14) and C9orf72 patient (ALS-52) were transduced at DIV28 with LV-GFP, LV-RuvBL1, or LV-RuvBL2 at an MOI of 10. 7 d post transduction proteins were extracted for analysis via immunoblot and MSD-ELISA. Transduction and overexpression of RuvBL1. (B, C) RA, Retanoic Acid; CHIR, CHIR99021; Pur, Purmophamine; MN, motor neuron (B) and RuvBL2 (C) were confirmed via immunoblot with GAPDH indicating equal loading. Levels of RuvBL1 or RuvBL2 were quantified relative to Tg GFP-transduced samples. (D) Levels of poly(GA) DPRs were assessed by MSD-ELISA (mean ± SEM, N = 3 independent experiments; one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test: *P < 0.05, ns, non-significant). (E) Levels of poly(GP) DPRs were assessed by MSD-ELISA (mean ± SEM, N = 3 independent experiments; one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test: ns, non-significant).