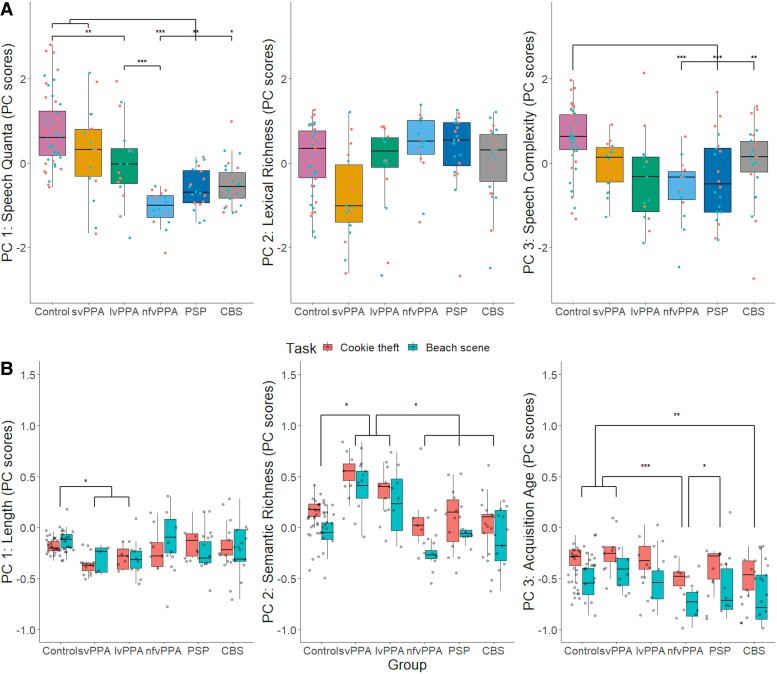
Figure 1.
PCA scores across diagnostic groups. (A) Scores of quantitative measures of speech fluency. For PC 1 (‘speech quanta’), the results from a one-way ANOVA revealed significant group differences [F(1142) = 71.19, P < 0.001], driven by controls (N = 24) and patients with svPPA (N = 9) having higher scores than those with nfvPPA (N = 9), PSP (N = 10) and CBS (N = 13), controls having higher scores than those with lvPPA (N = 9) and patients with lvPPA having higher scores than those with nfvPPA. PC 2 (‘lexical richness’) resulted in no group differences [F(1142) = 1.26, P = 0.26], and for PC 3 (‘speech complexity’), significant group differences were found [F(1142) = 12.77, P < 0.001], driven by controls having higher scores than patients with nfvPPA (P < 0.001), PSP (P < 0.001) and CBS (P = 0.002). (B) Scores of quantitative measures of word properties across groups. For PC 1 (‘length’), the results from a two-way ANOVA revealed significant group differences [F(5134) = 4.29, P < 0.001], driven by svPPA and lvPPA patients producing words that were shorter, phonologically and orthographically less complex than controls (P < 0.05). For PC 2 (‘semantic richness’), significant differences were found for group [F(5134) = 16.62, P < 0.001] and task [F(1134) = 22.05, P < 0.001]. Patients with svPPA and lvPPA produced more words that were characterized as more frequent and semantically diverse than those with nfvPPA, PSP, CBS and controls (P < 0.01). For PC 3 (‘acquisition age’), significant differences were found for group [F(5134) = 7.09, P < 0.001] and task [F(1134) = 50.24, P < 0.001]. Post hoc analyses revealed that (i) nfvPPA patients produced words that were characterized as significantly earlier acquired than those with svPPA (P < 0.001), PSP (P = 0.05) and controls (P < 0.001) and (ii) CBS patients used words that were significantly earlier acquired than those with svPPA (P = 0.002) and controls (P = 0.01). Results from post hoc analyses using Tukey’s honestly significant difference test for multiple comparisons are shown as asterisks indicating level of significance: *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. CBS, corticobasal syndrome; lvPPA, logopenic variant of primary progressive aphasia; nfvPPA, non-fluent variant of primary progressive aphasia; PC, principal component; PSP, progressive supranuclear palsy; svPPA, semantic variant of primary progressive aphasia.