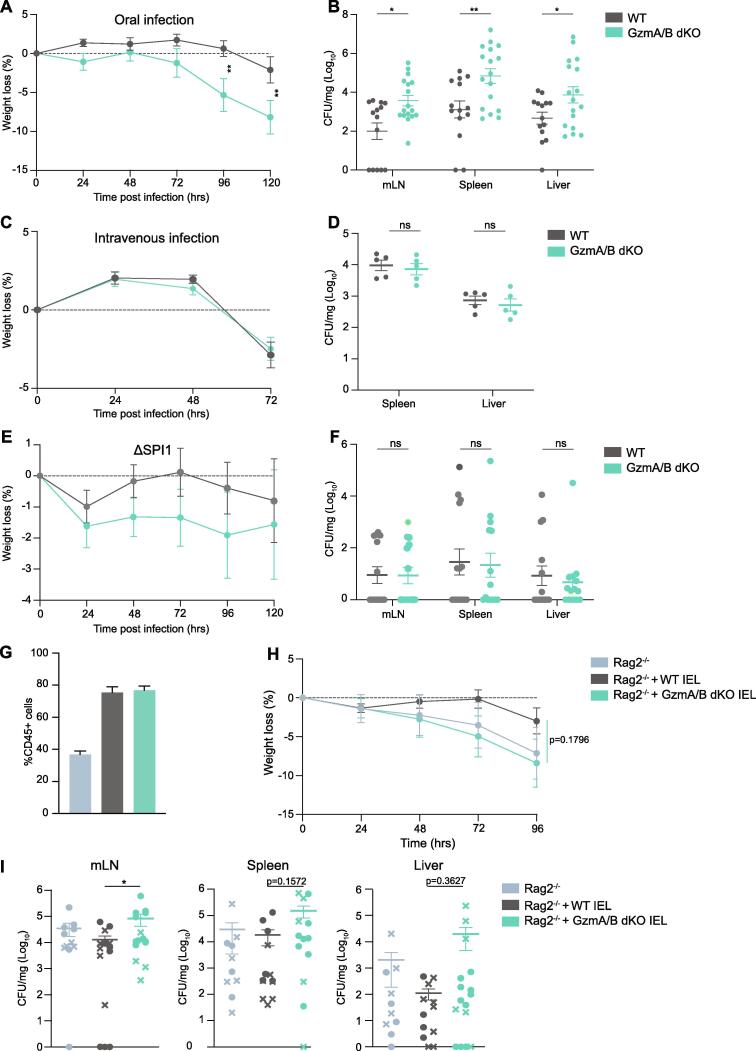
Fig. 2.
Granzymes are important for protection against oral intestinal infection. A-B. Cohoused WT (n = 14) and GzmA/B dKO (n = 17) mice were orally infected with SL1344-GFP and culled 5 days post infection (dpi). Weight loss (A) and CFU/mg in mLN, spleen and liver at the time of sacrifice (B) are shown. Data were pooled from 3 independent experiments. C-D. Cohoused WT and GzmA/B dKO mice were infected i.v. with SL1344-GFP and culled 3 dpi. Weight loss (C) and CFU/mg in spleen, liver at the time of sacrifice (D) are shown (n = 5/group). E-F. Cohoused WT and GzmA/B dKO mice were orally infected with ΔSPI1-SL1344 and culled 5dpi. Weight loss (E) and CFU/mg in mLN, spleen and liver are shown (F). Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments (n = 14/group). G-I. Rag2-/- mice were adoptively transferred with either WT (n = 12) or GzmA/B dKO IEL (n = 15) from cohoused mice, or no IEL (n = 10). 4 weeks after IEL transfer mice were orally infected with SL1344-GFP. (G) Percentages of CD45 + cells out of total live cells isolated from the intestinal epithelia of Rag2-/- mice, Rag2-/- mice reconstituted with WT IEL, and Rag2-/- mice reconstituted with GzmA/B dKO IEL after infection. Data were pooled from two independent experiments, where infected mice were either culled 4 or 5 dpi, depending on the severity of symptoms. Weight loss (H) and CFU/mg (I) in mLN (left), spleen (middle) and liver (right) are shown. In (I), cfu data from the two independent experiments culled 4dpi (circles) or 5dpi (crosses) are indicated. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. For bacterial counts, ranks were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test. ns: not significant, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.