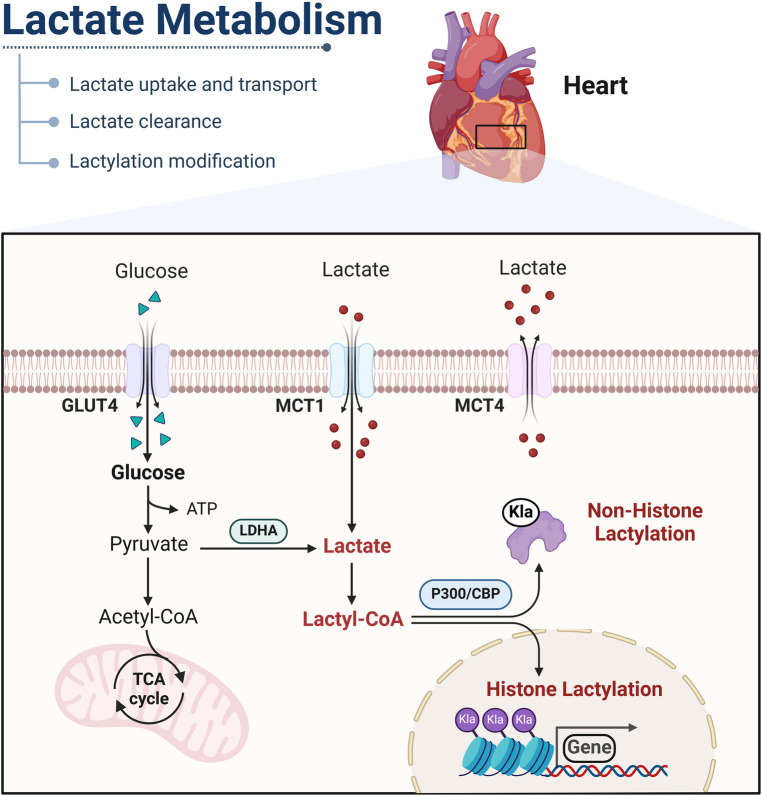
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of lactate metabolism and lactylation in cells. Lactate is transported into the cytoplasm via MCT or produced through glycolysis. In the cytoplasm, lactate catabolism occurs through two pathways. In one pathway, lactate is oxidized to pyruvate, which enters mitochondria and is metabolized through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. In the other pathway, lactate can be converted into lactyl-CoA and is involved in the lactylation of histones and nonhistone proteins. GLUT, glucose transporter, Klalysine lactylation; MCT, monocarboxylic acid transporter; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A. This figure is created with BioRender.com.