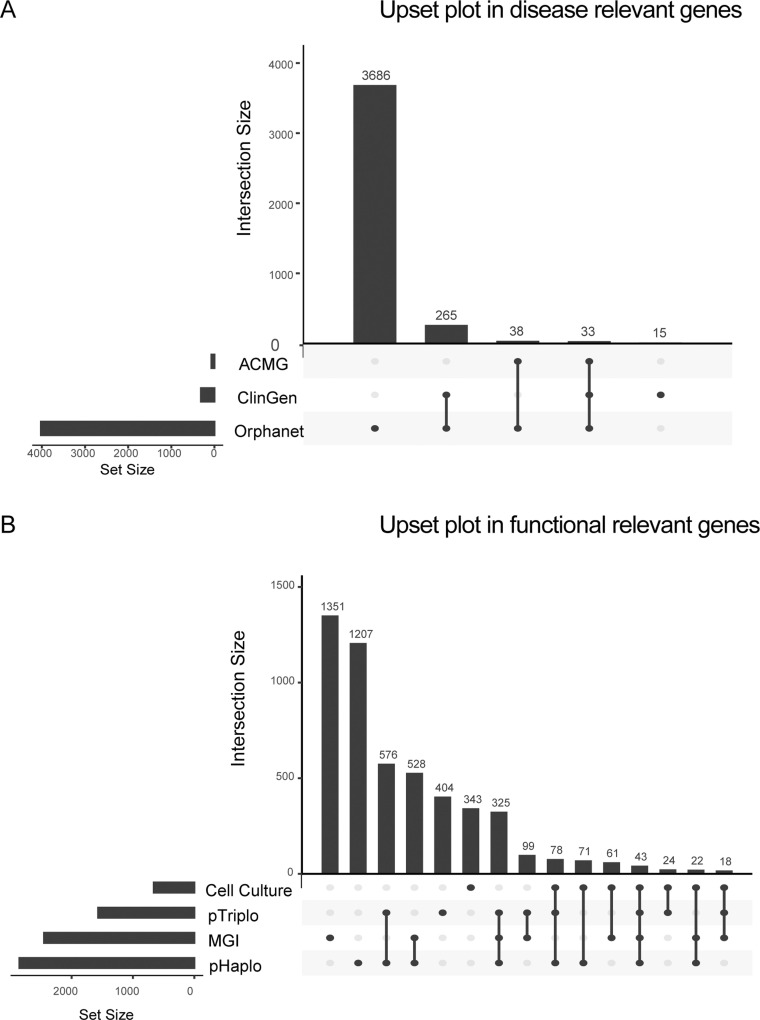
Figure S1. Distribution and intersection analyses of disease-relevant and functionally relevant genes.
(A) Upset plot showing the distribution and overlap of disease-relevant gene sets across three databases: ACMG (American College of Medical Genetics), ClinGen (Clinical Genome Resource), and Orphanet. Vertical bars indicate the size of each intersection, while horizontal bars represent the total number of genes in each database. The largest group is unique to ClinGen (3,686 genes), with additional smaller overlaps across combinations of the three datasets. (B) Upset plot of functionally relevant genes across four experimental and phenotypic databases: cell culture, pTriplo (probability of triplosensitivity), MGI (Mouse Genome Informatics), and pHaplo (probability of haploinsufficiency). The highest number of unique genes is in cell culture (1,351 genes), with other notable intersections among database combinations. Vertical bars show intersection sizes, while horizontal bars display total gene counts in each dataset.