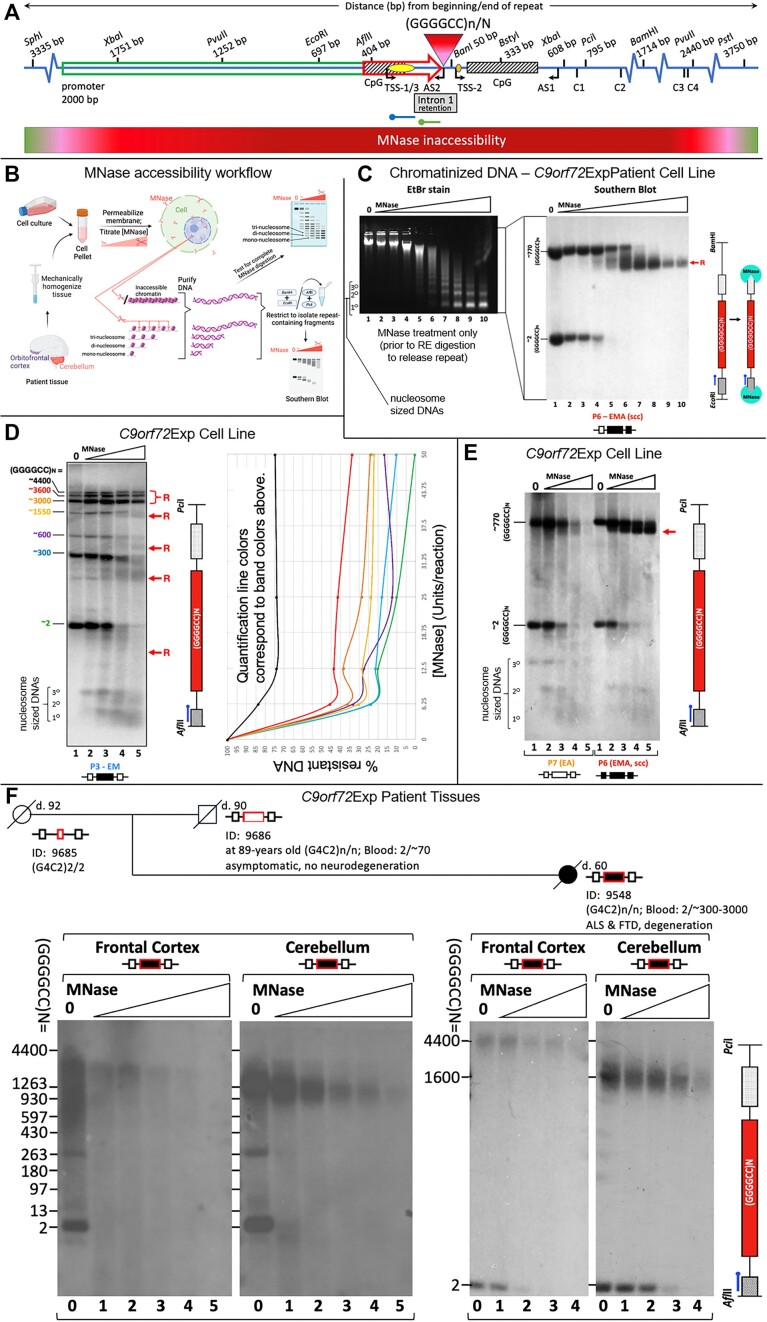
Figure 5.
C9orf72Exp locus is MNase-inaccessible. (A) Schematic of the region of unusual chromatin organized as determined by MNase accessibility analysis in C9orf72-ALS patient cells and brain regions. C9orf72 (GGGGCC)n-N repeat, CpG-islands (hatched boxes), long-2 kb and intermediate 435 bp promoters (green and red arrows, respectively), exons 1a (yellow dot) and 1b (orange dot), sense and antisense transcription start sites, restriction sites with distances from the beginning and end of the (GGGGCC)N tract, and probes for upstream (green) and downstream (blue) mapping of MNase accessibility. Cryptic splice site transcripts C1-C4 derived from the C9orf72Exp allele are indicated with their distance from the end of the repeat tract (42,45). (B) Workflow for MNase assay. (C) MNase treatment of chromatinized DNA from a cell line (P6) with a large methylated C9orf72Exp that had undergone single-cell cloning (scc) to isolate a single expanded allele, ensuring a single expansion size and facilitating clarity. EtBr staining of the MNase-treated DNA reveals over-digestion of the DNA to mono-, di- and tri-nucleosomal, sized fragments. The same DNA was digested with EcoRI/BamHI, to release the repeat fragment having 697 bp upstream and 1714 bp downstream of the repeat, then assessed by Southern blotting using the blue probe. Resistance of only the expanded allele occurs, even at high concentration of MNase (200U). Red ‘R’ indicates the region with reduced MNase accessibility that is about to lose the probed region indicated in the schematic at right. (D) Sample P3 with a mixture of heterogeneous repeat allele lengths shows that with increasing repeat size, MNase accessibility is decreased, as quantified by densitometric analysis for each allele size (colours coordinate between graph and Southern blot). In panels D–F the repeat was released with AflII/PciI, leaving 404 bp upstream and 689 bp downstream allowing increased resolution. NB, van Blitterswijk uses XbaI/XbaI to release the repeat, leaving 1751 bp upstream and 608 bp downstream of the repeat, the greater amount of flanking sequence reduces electrophoretic resolution. (E) Methylation is associated with increased MNase inaccessibility as assessed in cell lines (P6 [ssc] and P7) containing similar sized repeats but differing methylation status. The non-expanded allele is digested at the same rate in both lines. (F) MNase treatment of post-mortem (orbito)frontal cortex and cerebellum from an asymptomatic 90-year-old father and his ALS-FTD-affected daughter, previously deep-phenotyped for lifestyle choices, clinical, neuropathological and molecular biomarkers (29,70) (summarized in Supplementary Table S2). MNase concentrations are doubled between each lane (2.5U in lane 2 up to 40U). Expanded allele in both tissues is MNase resistant relative to the equimolar non-expanded allele, which serves as an internal control. See Supplementary Figure S4 for MNase controls and mapping experiments.