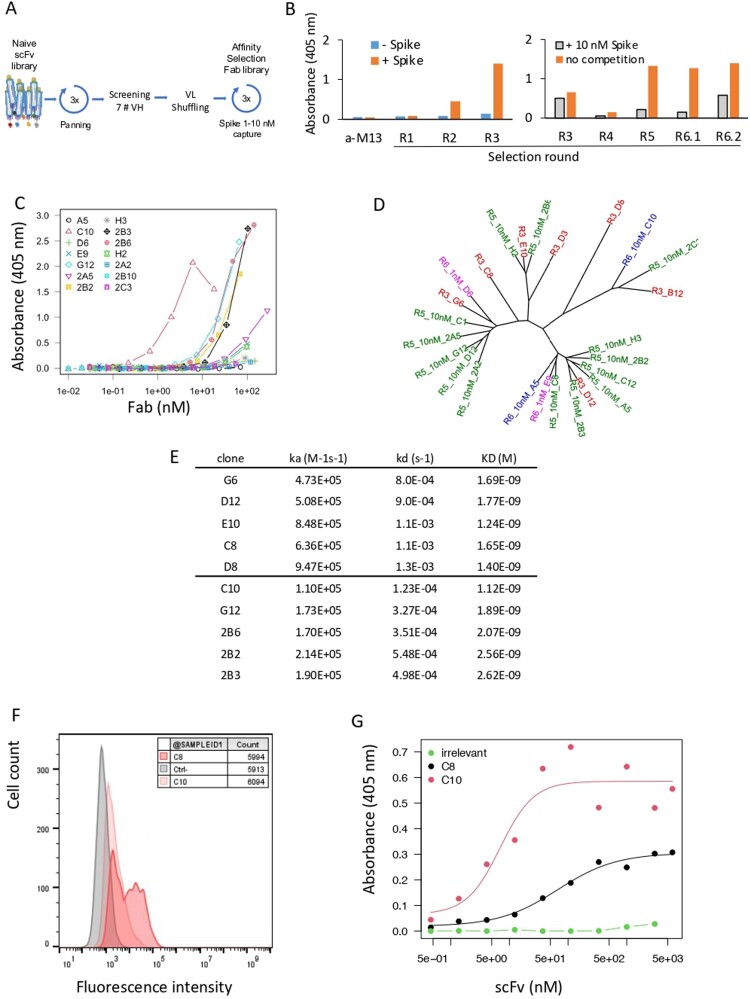
Figure 1.
Antibody discovery. (A) Antibody selection against SARS-CoV-2-Spike. A large naive synthetic scFv library was used for three consecutive rounds of biopanning on recombinant Wuhan Spike RBD captured by its poly-Histidine tag in microtiter plates. (B) ELISA of pool of phages (1011 phages/well) eluted after each round of selection. Phages were detected using an HRP-coupled anti-M13 monoclonal antibody (Sino Biological #11973-MM05T-H). Bars represent the absorbance obtained by ELISA. (Left): Initial selection of the naive library (rounds R1, R2, R3). Absorbance of the ELISA on Spike RBD-coated (orange) or non-coated (blue) plates. (Right): Pool of phages selected after light-chain shuffling and selection (R4 to R6.2). Absorbance of the indicated phage stocks in an ELISA on RBD-coated plates (orange). Absorbance obtained with phage stocks first incubated with 10 nM of Spike RBD, then captured on RBD-coated plates (grey). (C) Binding capacity of 14 soluble selected Fabs recognizing Spike RBD determined by ELISA. (D) Phylogenic tree of selected clones. Parental clones isolated from R3, matured clones isolated from R5, R6.1 and R6.2 are depicted in red, green, blue and purple, respectively. (E) Affinity of 10 selected clones to monomeric RBD measured by SPR. (F) Binding of C8 and C10 IgGs to HEK293 cells stably expressing Wuhan Spike at the cell surface. C8 and C10 mAbs were used at 10 µg/mL and detected using an AF647-coupled anti-human antibody. Grey histogram: isotype antibody control. (G) Dose-response binding to RBD of purified scFv C8 and C10, assayed by ELISA.