Fig 1.
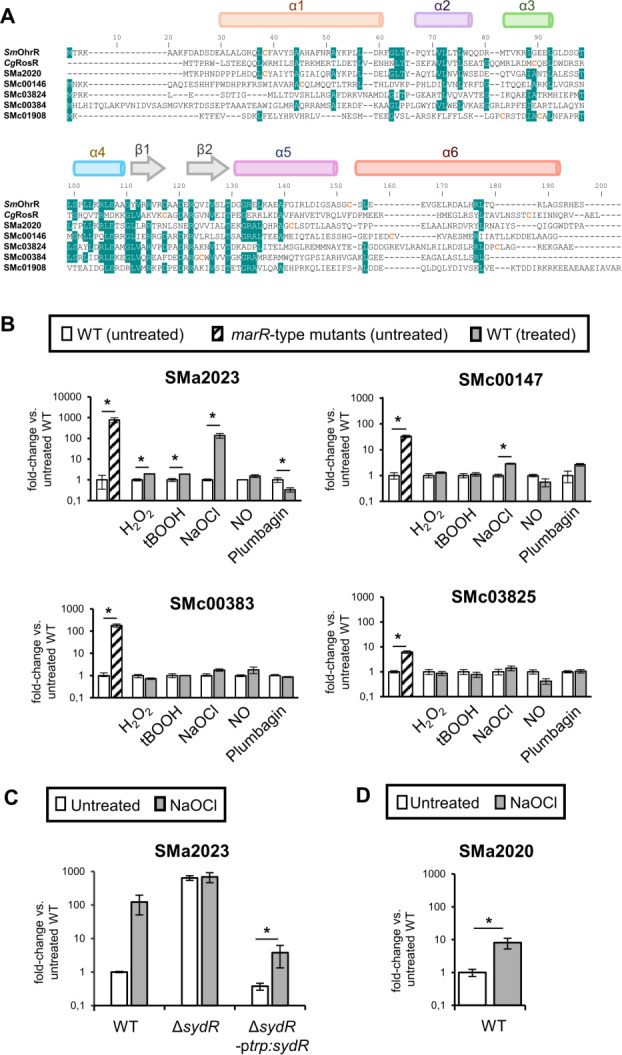
SydR is a new MarR-type redox-sensing repressor. (A) Sequence alignment of MarR-type regulators. The alignment between S. meliloti OhrR and SMa2020, SMc00146, SMc03824, SMc00384, SMc01908 products, and Corynebacterium glutamicum RosR, was generated using Clustal-W. Secondary structure elements were predicted from the sequence of SMa2020 product using Jalview (23). The HTH domain corresponds to helices α3 and α4, the wing to β-strands β1 and β2, and the dimerization region is formed by helices α1, α5, and α6. Cysteine residues are indicated in orange. Blue shading indicates an identity ≥70% at that position. (B) Analysis of MarR-type-mediated gene expression. RT-qPCR analysis of the expression of SMa2023, SMc00147, SMc00383, and SMc03825, considered as potential target genes of SMa2020, SMc00146, SMc00384, and SMc03824 products, respectively. The expression of each gene was analyzed in wild-type strain (WT) and related marR-type mutant under control condition (untreated) and in WT challenged with H2O2, tBOOH, NaOCl, NO or plumbagin (treated). (C) The induction of SMa2023 expression by NaOCl is SydR-dependent. RT-qPCR analysis of SMa2023 expression in WT, ΔsydR (SMa2020-inactivated mutant) and ΔsydR-ptrp:sydR strains under control conditions (untreated) or challenged with NaOCl. (D) SMa2020 expression is induced by NaOCl. RT-qPCR analysis of SMa2020 expression in the WT strain under control condition (untreated) or challenged with NaOCl. (B–D) For each condition, transcription levels were normalized to those in untreated WT. The values shown are the means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Student’s t test was used to assess the statistical significance (*P < 0.05).
