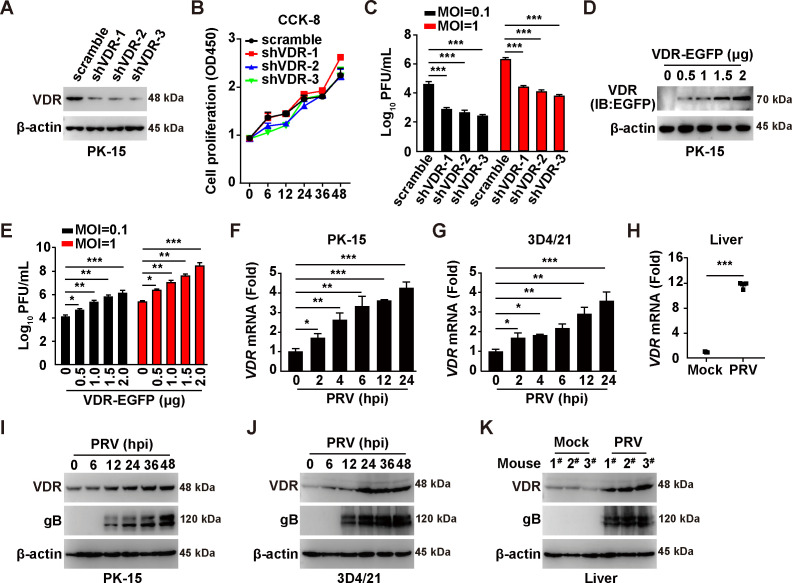
Fig 1.
PRV infection upregulates VDR expression to promote viral proliferation. (A) The protein levels of VDR in scramble, shVDR-1, shVDR-2, and shVDR-3 PK-15 cells were analyzed by immunoblotting analysis. (B) Cell proliferation was analyzed in scramble, shVDR-1, shVDR-2, and shVDR-3 PK-15 cells for 0–48 h by CCK-8 assay. (C) Scramble, shVDR-1, shVDR-2, and shVDR-3 PK-15 cells were infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1 and 1) for 24 h. The viral titer was analyzed by a PFU assay. ***P < 0.001. (D) PK-15 cells were transfected with VDR-EGFP plasmid (0–2 µg) for 24 h. VDR-EGFP expression was analyzed by immunoblotting analysis. (E) PK-15 cells were transfected with VDR-EGFP plasmid (0–2 µg) for 24 h. Cells were then infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1 and 1) for another 24 h. The viral titer was analyzed by a PFU assay. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (F and G) PK-15 (F) and 3D4/21 (G) cells were infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 1) for 0–24 h. The mRNA levels of VDR were analyzed using qRT-PCR analysis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (H) C57BL/6 J mice were mock‐infected or intranasally infected with PRV-QXX (5 × 103 TCID50 per mouse) for 3 days. The mRNA levels of VDR in murine liver were analyzed by qRT-PCR analysis (n = 3). ***P < 0.001. (I and J) PK-15 (I) and 3D4/21 (J) cells were infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1) for 0–48 h. VDR, gB, and β-actin were analyzed by immunoblotting analysis. (K) The protein levels of VDR, gB, and β-actin were analyzed by immunoblotting analysis in murine liver from (H).