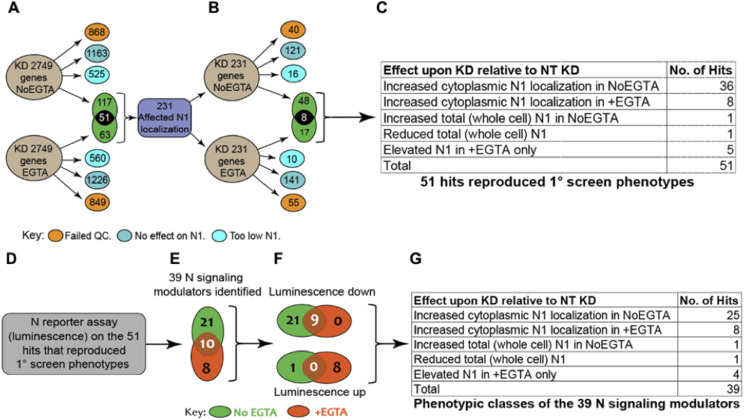
Figure 4. Schematics of the screens and of the candidate gene classification process.
(A) A total of 2,749 genes were silenced in the primary screen. Candidates that, when compared with controls, led to marked cytotoxicity, did not affect intracellular NOTCH1 (N1) localization, or caused general loss of NOTCH1 signal, were excluded from further analysis (orange, blue, and light blue circles, respectively). A total of 231 genes that altered intracellular NOTCH1 localization were identified (green). 117 did so in unstimulated condition, 63 upon EGTA stimulation and 51 in both conditions. (B) The 231 candidates underwent secondary screening. 73 of the 231 led to changes in NOTCH1 localization, but only 51 genes reproduced the primary screen phenotypes. (C) Of these 51, 38 affected NOTCH1 trafficking in the unstimulated No EGTA condition, 13 altered NOTCH1 trafficking in the stimulated +EGTA condition. (D, E) MCF10A-RbpJk-Luc Notch reporter assay identifies 39 candidates that affect Notch signaling. (F) Of the 39, 30 suppress Notch signaling, whereas nine enhance Notch signaling. (G) Classification of the 39 candidates by their effect on intracellular NOTCH1 (N1) localization and/or levels.