Extended Data Figure 3: Co-transplantation of breast cancer cells with DRG neurons drives metastasis.
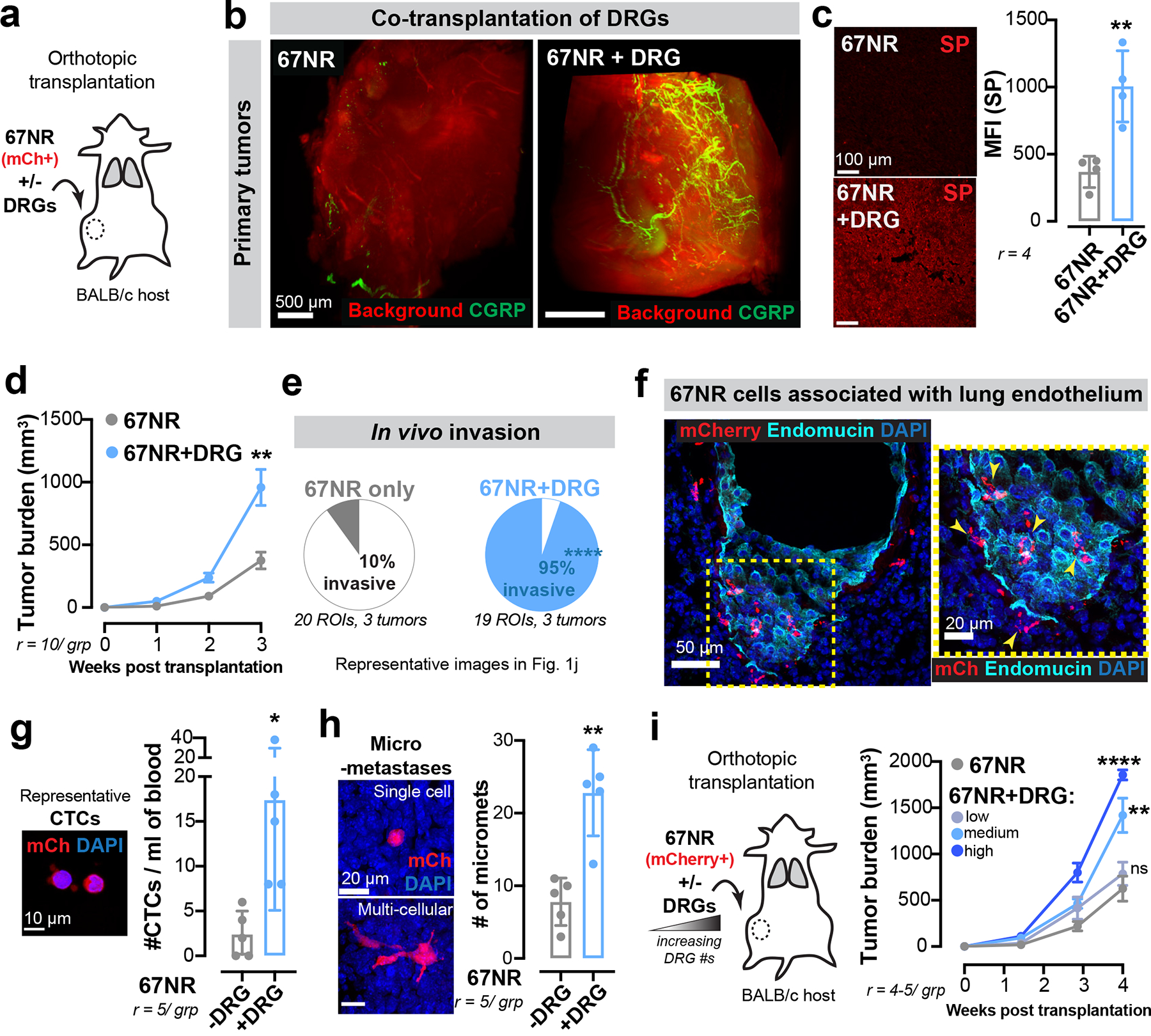
(a-h) Co-transplantation of mCherry+ (mCh) 67NR cancer cells and DRG neurons. (a) Schematic. (b) Optically cleared 67NR tumours transplanted with or without DRG neurons and immunostained for CGRP+ sensory nerves. r = 2 tumours/ group. (c) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for SP in 67NR primary tumours transplanted with or without DRG neurons. **p = 0.0046, t-test. Mean ± SD. (d) Tumour growth. **p = 0.0017, t-test. Mean ± SEM. (e) Percentage of the tumour-stroma boundary with a pushing vs invasive morphology. ****p < 0.0001, Chi-square test. (f) Association of mCh+ 67NR cancer cells with the lung endothelium in mice transplanted with orthotopic 67NR tumours. r = 3 lungs/ group. (g) CTC enumeration in mice transplanted with mCh+ 67NR cancer cells with or without DRG neurons. *p = 0.0287, t-test. Mean ± SD. (h) mCh+ micro-metastases. **p = 0.0079, Mann-Whitney test. Mean ± SD.
(i) Co-transplantation of 67NR cancer cells with increasing numbers of DRG neurons. nsp = 0.4124, **p = 0.0026, ****p < 0.0001, ANOVA. Mean ± SEM.
