Fig. 4 |. Replication-associated genetic instability induced by non-B DNA.
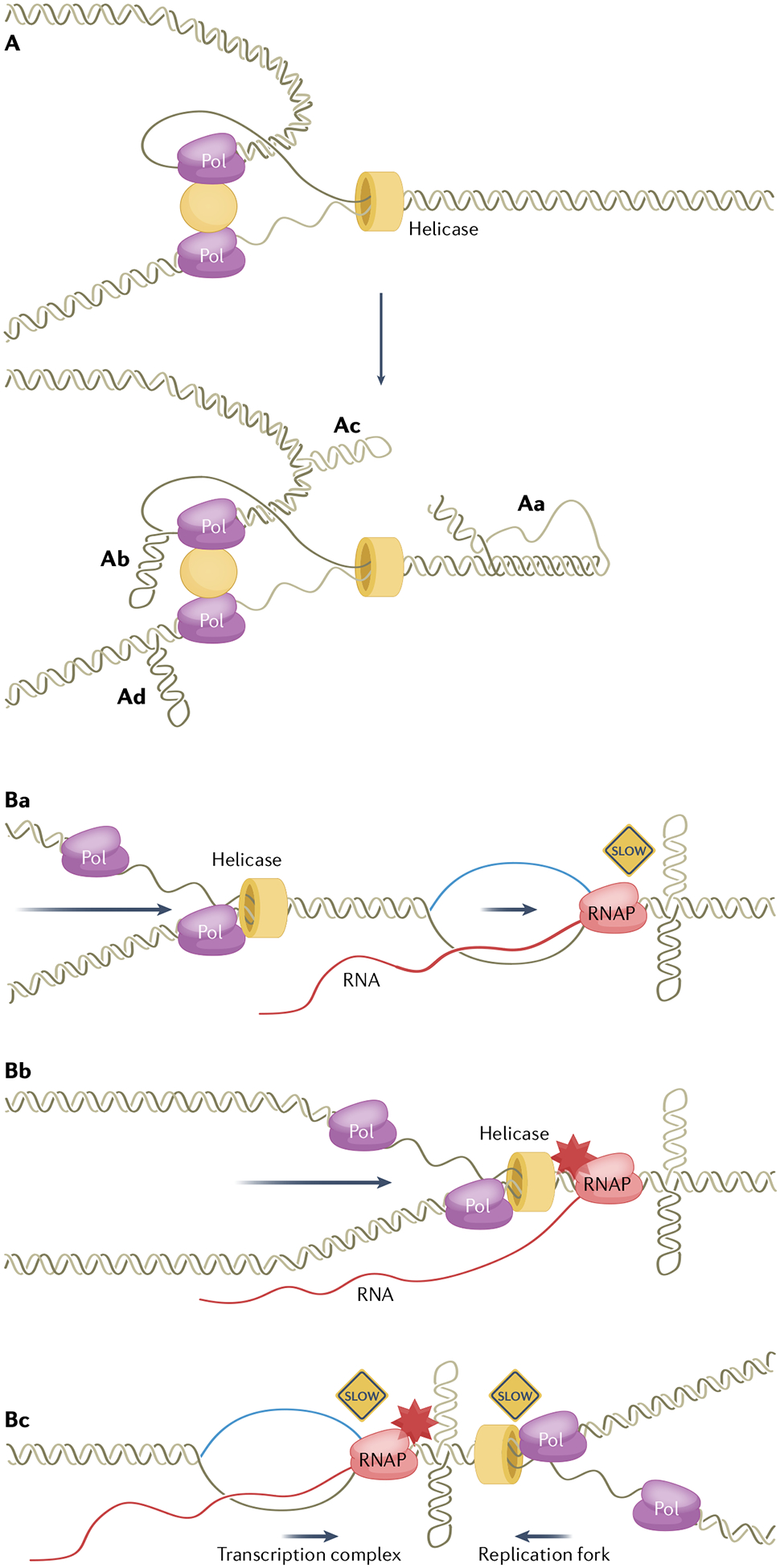
A, Non-B DNA formed at a progressing replication fork. A progressing DNA replication fork is depicted on the top. Aa, A non-B DNA structure (shown in the schematic as H-DNA) in front of a replication fork slows or stalls replication, which gives rise to further structural alterations on the replication complex. Ab, A hairpin structure formed on the template of a lagging strand can lead to replication stalling or repeat contraction (repeat template skipping). Ac, Ad, Hairpin structures formed on the nascent strands on the leading and lagging strands can lead to repeat expansion (via nascent strand self-folding and misalignment). B, Non-B DNA-induced transcription and replication collisions. Ba, Transcription and replication forks in the same direction. Bb, Non-B DNA (shown as a cruciform structure) slows or stalls transcription elongation and leads to a co-directional collision. Bc, Non-B DNA slows or stalls replication or transcription and disrupts the coordination, leading to headon collisions. Collisions in either direction can lead to replication stress and genetic instability. RNAP, RNA polymerase; Pol, DNA polymerase.
