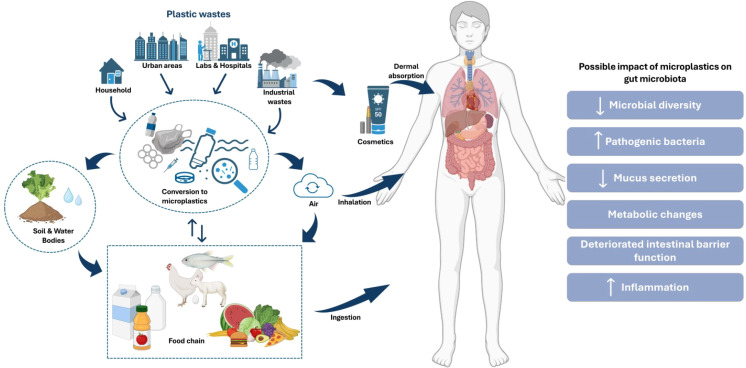
Figure 2.
Pathways of microplastic (MP) exposure and its impact on human gut microbiota. The figure illustrates the sources of plastic waste and their transformation into MPs which enter the human body through ingestion, inhalation, and dermal absorption. It also depicts the possible impacts of MPs on gut microbiota, including reduced microbial diversity, increased pathogenic bacteria, altered mucus secretion, metabolic changes, impaired intestinal barrier function, and increased inflammation (Covello et al., 2024; Demarquoy, 2024).