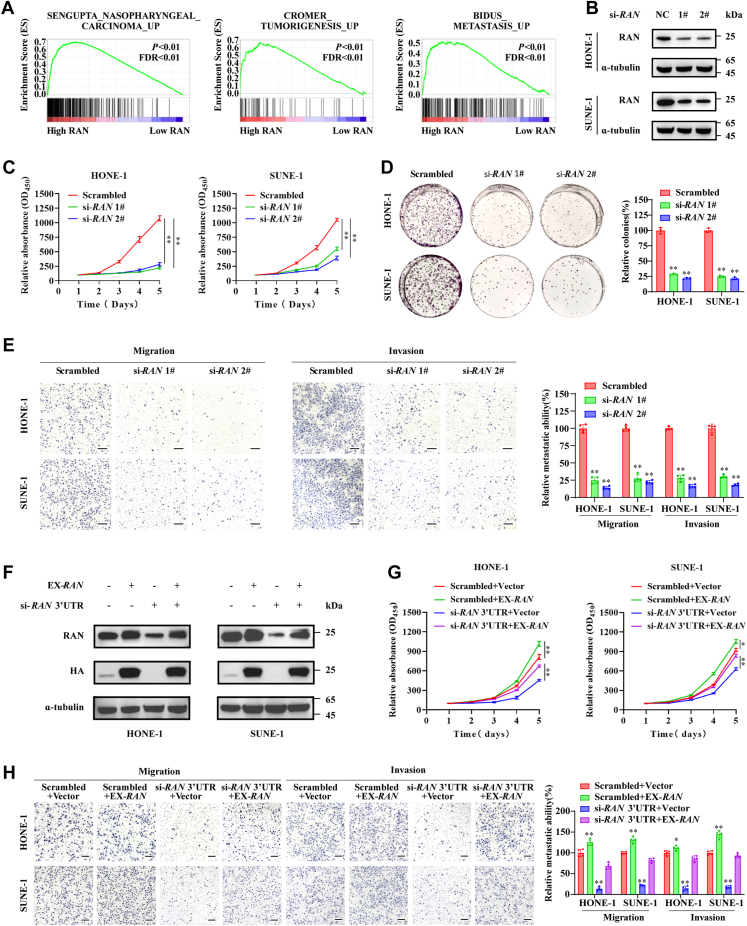
Figure 2.
RAN facilitates NPC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro.A, GSEA based on data from the GEO database (GSE53819) found that RAN expression levels were positively correlated with NPC progression and metastasis. B, siRNA-mediated interference was used to knockdown RAN in HONE-1 and SUNE-1 cells, and Western blotting was applied to validate knockdown efficiency. C, cell proliferation ability was evaluated by CCK-8 assays in HONE-1 and SUNE-1 cells after silencing of RAN. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 6). D, cell proliferation ability was evaluated by colony formation assays in HONE-1 and SUNE-1 cells after silencing of RAN. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). E, migration and invasion capacity were analyzed by transwell assays in RAN-silenced SUNE-1 and HONE-1 cells. The scale bar represents 200 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 4). F, Western blotting was applied to confirm the cotransfection efficiency of scrambled control or siRNA-targeting RAN 3′ UTR, together with empty vector or HA-tagged RAN overexpression vector. G, cell proliferation was evaluated by CCK-8 assays in SUNE-1 and HONE-1 cells after cotransfected with scrambled control or si-RAN 3′ UTR, together with empty vector or HA-tagged RAN overexpression vector. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 6). H, migration and invasion capacity were analyzed by transwell assays in SUNE-1 and HONE-1 cells after cotransfected with scrambled control or si-RAN 3′ UTR, together with empty vector or HA-tagged RAN overexpression vector. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 4). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. The significant differences were assessed using one-way ANOVA (D, E, and H) and two-way ANOVA (C and G). CCK-8, Cell Counting Kit-8; GEO, Gene Expression Omnibus; NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma; GSEA, gene set enrichment analysis; HA, hemagglutinin.