Fig. 3.
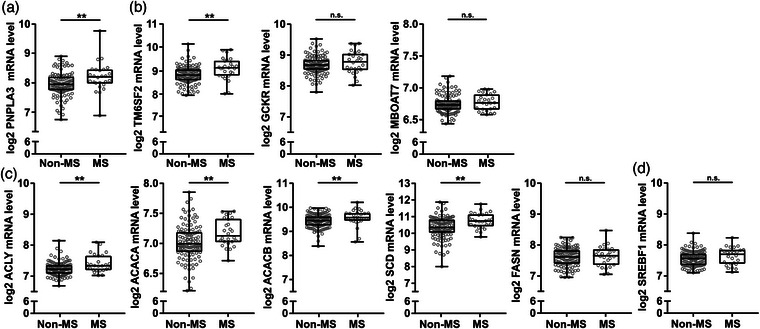
Hepatic levels of metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD)‐ and de novo lipogenesis (DNL)‐associated transcripts were higher in human metabolic syndrome patients. Liver biopsy homogenates from individuals without known liver disease and without statin therapy were analyzed using human transcriptome array and grouped by meeting criteria for the metabolic syndrome (MS) or not (non‐MS). (a and b) Transcript levels of MASLD associated genes patatin‐like phospholipase domain containing 3 (PNPLA3), transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 (TM6SF2), glucokinase regulator (GCKR), and membrane bound O‐acyltransferase domain containing 7 (MBOAT7). (c) Transcript levels of key enzymes involved in DNL ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), acetyl‐CoA carboxylase alpha (ACACA), ACACB, stearoyl‐CoA desaturase (SCD), and FASN. (d) Transcript levels of SREBF1 transcriptional regulator of DNL associated genes. Data are expressed as min to max box plots with middle line at median, each dot represents one patient. Mann Whitney U test. n.s., not significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 (n = 26–115/group).
