Figure 8.
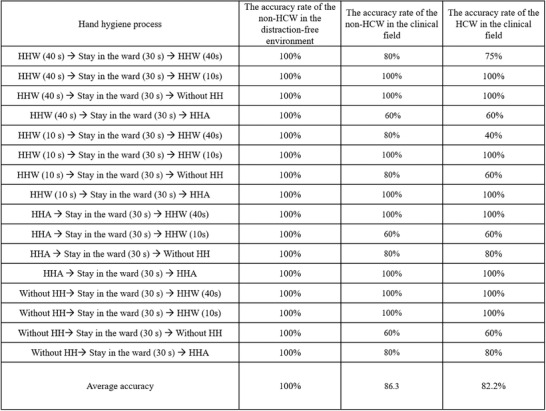
Accuracy rates for 16 possible basic hand hygiene behaviors in sandbox simulation tests conducted in different environments by non‐HCWs and HCWs. The processes involve various combinations of handwashing (HHW) for 10 or 40 s, hand antisepsis (HHA), and periods of staying in the ward for 30 s, with or without hand hygiene (HH) steps. The table records accuracy rates for these behaviors in a distraction‐free environment, a nonclinical field, and a clinical field for both non‐HCWs and HCWs. The average accuracy across all tested behaviors was 100% for non‐HCWs in a distraction‐free environment, 86.3% for non‐HCWs in the clinical field, and 82.2% for HCWs in the clinical field. This suggests that the complexity of the environment may affect adherence to hand hygiene processes, particularly for HCWs.
