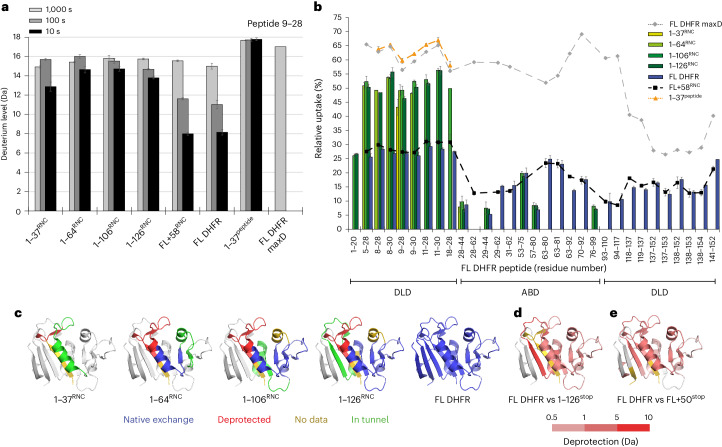
Fig. 3. Conformational dynamics of nascent DHFR on the ribosome.
a, Deuterium incorporation into peptide 9–28 of DHFR as a function of deuterium exposure time and NC length. Data are presented as mean values of two to four replicates. Error bars, s.d.; n = 3 or n = 4 independent experiments. b, Relative deuterium uptake of DHFR peptides after 10 s exposure to deuterium. Peptides belonging to the DLD or ABD subdomains are indicated. Data are presented as mean values of two to four replicates. Error bars, s.d.; n = 3 or n = 4 independent experiments. c, Peptide-resolved folding of nascent DHFR, illustrated on the structure of native DHFR (PDB 5CCC). Peptides with the same deuterium uptake (within 0.5 Da) as the native controls (FL DHFR or FL + 58RNC) are colored blue, while peptides that are deprotected relative to the controls are colored red. Regions for which we did not measure HDX are colored gold. The C-terminal 22 aa in each construct, expected to be occluded in the exit tunnel at that chain length, is colored green. The part of DHFR that is not yet synthesized at each chain length is colored white. d, Difference in deuterium uptake between FL DHFR and 1–126stop after 10 s deuteration. Darker red indicates more deuterium in 1–126stop relative to FL DHFR (increasing deprotection). Residues 127–159, not present in 1–126stop, are colored white. e, Difference in deuterium uptake between FL DHFR and FL + 50stop after 100 s deuteration. Darker red indicates increasing deprotection of FL + 50stop relative to FL DHFR. Peptides that do not differ in exchange are colored white. See also Extended Data Fig. 4 and Supplementary Data 1.