Figure 1.
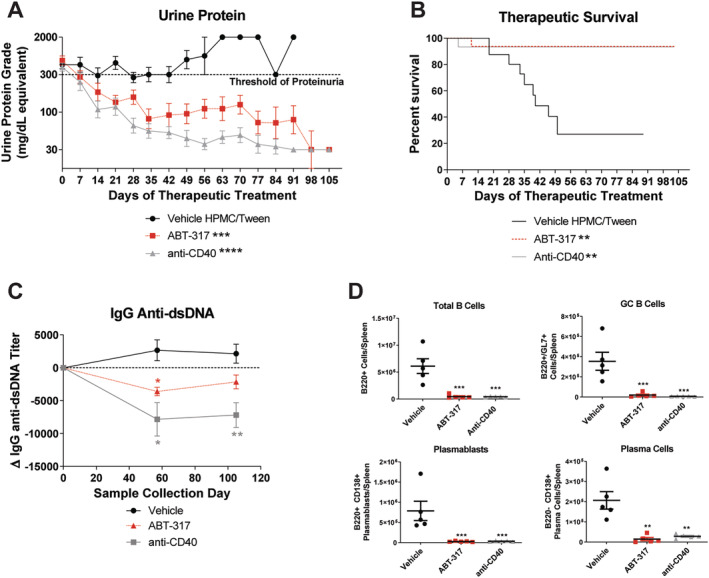
ABT‐317 reversed severe proteinuria, circulating anti‐dsDNA antibody titers, and splenic B cell subsets. Therapeutic oral treatment of female NZB/W‐F1 mice with vehicle (n = 19), 60 mg/kg SID of ABT‐317 (n = 16), or 15 mg/kg of anti‐CD40 (n = 15) began when mice became severely proteinuric. (A) The average urine protein is graphed and ABT‐317 shows reversal of proteinuria comparable to 15 mg/kg of anti‐CD40; **P < 0.01 vs vehicle ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 vs vehicle using one‐way ANOVA, Kruskall‐Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparisons. (B) Survival percentage showing 95% survival in ABT‐317‐treated mice; **P < 0.01 vs vehicle using log‐rank Mantel‐Cox test. (C) ABT‐317 significantly reduced anti‐dsDNA antibody titers at study day 57; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 vs vehicle using mixed‐effects analysis with Tukey's multiple comparisons. (D) The number of B cells (B220+), splenic GC B cells (B220+/GL7+), plasmablasts (B220+/CD138+), and plasma cells (B220‐/CD138+) was determined at the end of the study by flow cytometry and significant reduction of each subset by ABT‐317 was observed; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs vehicle using one‐way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparisons. ANOVA, analysis of variance; dsDNA, double‐stranded DNA; GC, germinal center; HPMC, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose; SID, once daily.
