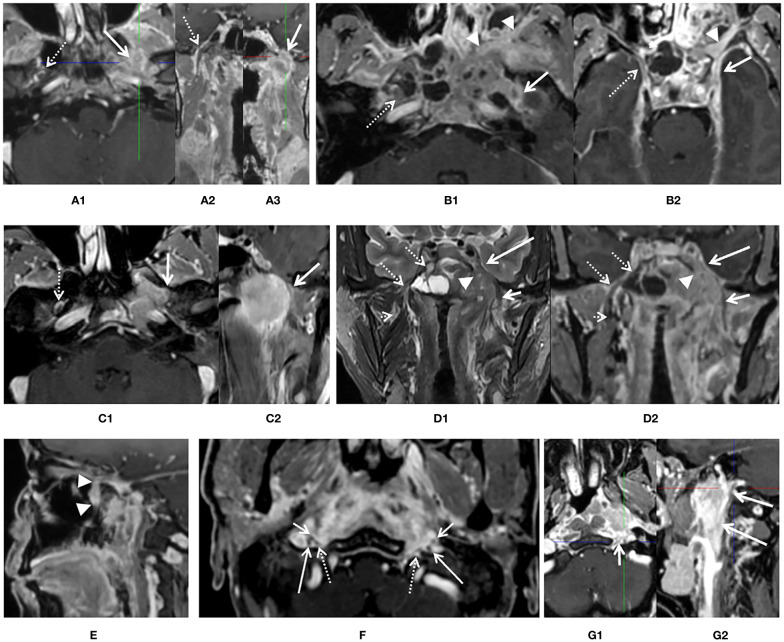
Figure 2.
Diagnostic criteria of perineural spread (PNS) by 3D_LAVA_flex on axial, reformatted sagittal, and coronal images. (A) An enhancement and enlargement of oval foramen of left side [(A1, A3), white solid arrow] and total disappear of low signal intensity of nerve which suggested an intraneural involvement of mandibular nerve, corresponding normal V3 division [(A1, A2), white dash arrow] was visible on the contralateral side. (B) Thickness and enhancement of left oval foramen and rotundum [(B1, B2), solid arrow] suggested PNS positive. Right side is clear (dash arrow). Whole pterygopalatine fossa involvement of left side was also seen (arrow head). (C) A thickness and encircle of V3 branch about ½ on left mandibular nerve (solid arrow) suggested infiltration of rotundum segment on axial (C1) and reformatted coronal (C2) image, right side is normal. (D) Whole left Meckel’s cavity (arrow head) and cavernous sinus (long solid arrow) involvement on coronal T2 weighted image (D1) and reformatted coronal image (D2) was presented and suggested left anterior cranial nerve involvement. Both extracranial and skull base segments of left V3 was also involved (short solid arrow). Meckel’s cavity (dash arrow) and cavernous sinus (dash arrow) on right side is normal. (E) Whole pterygopalatine fossa involvement of left side refers to as a sign of maxillary nerve involvement (arrow head). (F) At least one third of the extracranial segment of bilateral hypoglossal nerve (dash arrow) and CN IX–XI (long and short arrow) were involved or encircled by primary lesion in the upper carotid space. (G) At least one third of the extracranial segment of left hypoglossal nerve (short arrow) and CN IX–XI (long arrow) were involved or encircled by primary lesion in the upper carotid space, while not for right side.