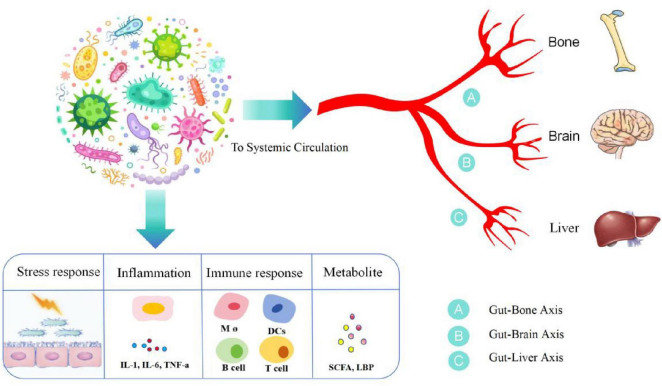
FIGURE 2.
Gut microorganisms and various distal organs constitute a pathway of influence, which we call axes, such as the gut-bone axis, the gut-brain axis, and the gut-hepatic axis. Gut microorganisms, under the influence of stress response, inflammation, immunity, etc., produce a variety of inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor, and a variety of immune cells, such as B cells, T cells, and monocytes, as well as the metabolites SCFA and LPS, which arrive at distal organs through the blood circulation and are involved in disease progression. IL-1, interleukin 1; IL-6, interleukin 6; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.