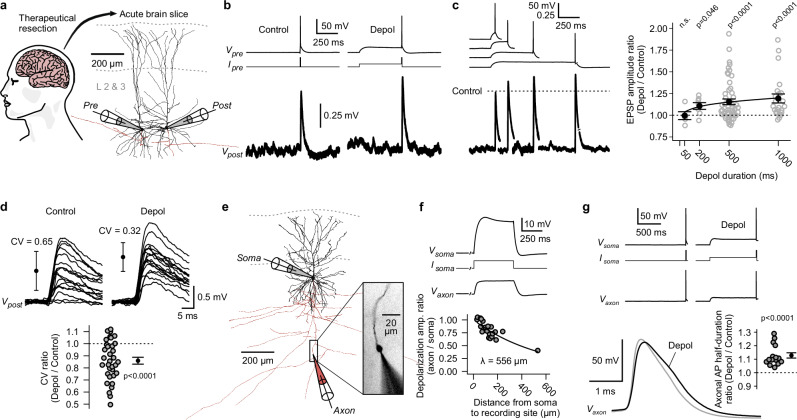
Fig. 1. Presynaptic subthreshold depolarizations increase synaptic strength through broadening of axonal action potentials.
a Schematic of the human neocortex and reconstruction of two pyramidal neurons, which were connected by a unitary synapse (Pre and Post stands for pre- and postsynaptic neuron). b Paired whole-cell patch-clamp recording of neurons shown in panel a. Current was injected into the presynaptic neuron to elicit action potentials (AP) from resting membrane potential (‘Control’) or after a subthreshold depolarization (‘Depol’). Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP) were averaged over multiple trials. c Four separate recordings with different durations of depolarizations. To visualize relative change of EPSP amplitudes, postsynaptic signals were normalized to the ‘Control’ condition of each recording (dotted line). Right, relative changes of EPSP amplitudes plotted against depolarization durations (p-values were computed using two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank tests; 50 ms, n = 5 paired recordings; 200 ms, n = 7; 500 ms, n = 53; 1000 ms, n = 23; error bars show mean ± s.e.m; fit line corresponds to bi-exponential function with time-constants for Kv1-inactivation, see Fig. 2d). d Top, single-trial EPSPs of an exemplary synapse (error bars show mean ± s.d. of single-trial amplitudes; traces were smoothed using a moving average with a 1 ms window; CV: coefficient of variation). Bottom, summary plot of relative changes of CVs (experiments with 500 or 1000 ms ‘Depol’-duration and effect > 1.1 in panel c were pooled; n = 34 paired recordings; two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test; error bar shows mean ± s.e.m). e Reconstruction of exemplary somato-axonal recording. Inset, axonal ‘bleb’ filled with Alexa Fluor 568 dye during recording. f Somato-axonal recording of the neuron shown in panel e. Current was injected at the soma to cause a subthreshold depolarization, which spread into the axon. Bottom, relationship between distances from soma and attenuation of amplitudes of passively spreading depolarizations (n = 20 somato-axonal recordings; mono-exponential fit). g Somato-axonal recording. APs were elicited at the soma. Bottom left, overlay of ‘Control’ and ‘Depol’ AP recorded in the axon. Bottom right, summary plot of relative changes of axonal AP half-durations (n = 15 somato-axonal recordings; two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test; error bar shows mean ± s.e.m). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.