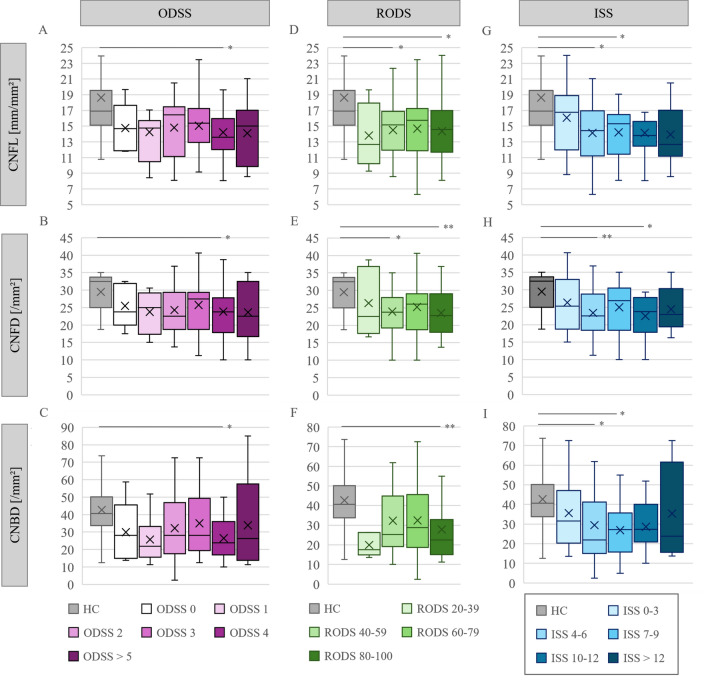
Fig. 3.
Comparison of CCM parameters with clinical scores of all CIDP patients with HC (n = 31). Comparison was performed using Kruskal Wallis test with Bonferonni correction. Significant reduction of CNFL (A: 14.2 ± 3.3, p = 0.004), CNFD (B: 23.8 ± 7.2, p = 0.014) and CNBD (C: 28.6 ± 16.3, p = 0.015) in patients with ODSS > = 4. Patients with RODS 76–100 showed significant reduction of CNFL (D: 14.2 ± 3.6, p = 0.003), CNFD (E: 23.3 ± 6.1, p = 0.001), and CNBD (F: 27.7 ± 15.9, p = 0.001). Patients with RODS of 51–75 showed significant reduction of CNFL (D: 14.5 ± 3.4, p = 0.009) and CNFD (E: 25.0 ± 7.1, p = 0.049). Patients with ISS sum score > = 11 showed significant reduction of CNFL (G: 14.1 ± 3.6, p = 0.002) and CNFD (H: 23.6 ± 6.1, p = 0.007). Patients with ISS sum score of 6 to 10 showed significant reduction of CNFL (G: 14.1 ± 3.1, p = 0.002), CNFD (H: 24.1 ± 6.8, p = 0.012), and CNBD (I: 27.9 ± 14.1, p = 0.004). Patients with ISS sum score of 0 to 5 showed significant reduction of CNFD (H: 24.8 ± 7.1,p = 0.019) and CNBD (I: 32.5 ± 19.0, p = 0.043). ODSS 0: n = 5; ODSS 1: n = 12; ODSS 2: n = 29, ODSS 3: n = 19; ODSS > = 4: n = 35. RODS 26–50: n = 21, RODS 51–75: n = 38, RODS 76–100: n = 37. ISS 0