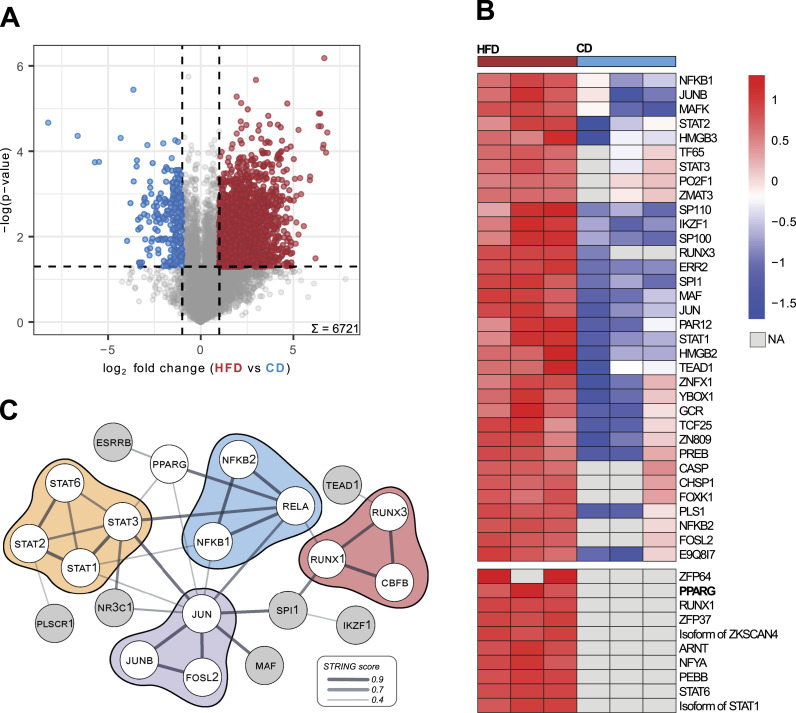
Figure 4. High-fat diet rewires the nuclear proteome in the mouse liver.
(A) Volcano plot showing the result of a permutation-based t test comparing protein intensities across biological replicates (n = 3) in control (left) and high-fat diet (right). Colored points denote significantly up-regulated proteins with a −log (P-value) cutoff of = 1.3 (FDR = 0.05) and a fold change cutoff of log2 1 for each diet (CD, blue; HFD, red). (B) Heatmap of z-scored protein intensities of quantified transcription factors across biological replicates (n = 3) in CD (right) and HFD (left) with exclusively quantified TFs in HFD in the bottom part. (C) String physical subnetwork of up-regulated and exclusive transcription factors in HFD. The TF list was loaded into the STRING app in the Cytoscape platform with Mus musculus as a model species and physical network type, and with default search parameters (0.4 confidence cutoff). Singletons were not shown, and only the main network was shown. After network generation, manual arrangement of nodes was performed. STAT proteins were colored yellow; NFkB-related, blue; JUN-related, purple; and RUNX-related, red.