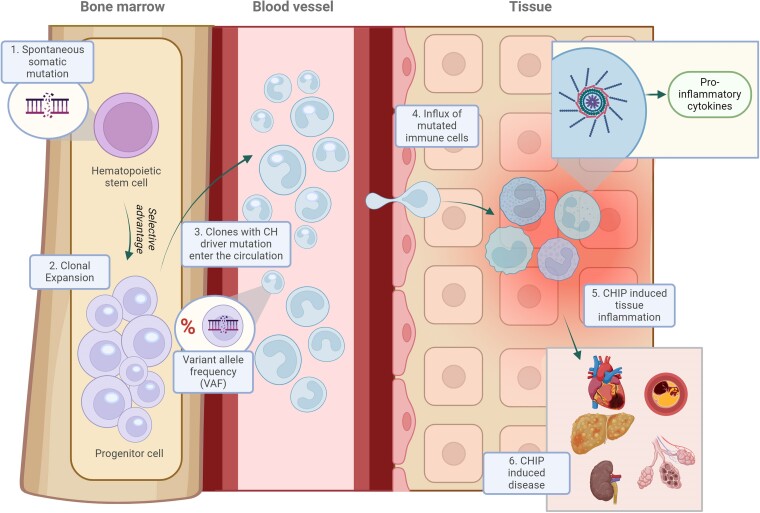
Figure 2.
The association between clonal haematopoiesis, inflammation, and disease development. Somatic mutations origin in haematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow due to environmental triggers or as a result of ageing (1). When the mutation affects a (driver) gene that provides the cell a competitive advantage, that cell can expand, leading to a mutant cell population (2). The size of the clone can be measured by the variant allele frequency (VAF). The mutated cell progeny enter the circulation (3) where they may infiltrate organ tissue (4) resulting in elevated levels inflammation (5) and consequently leading to tissue damage and organ failure (6)