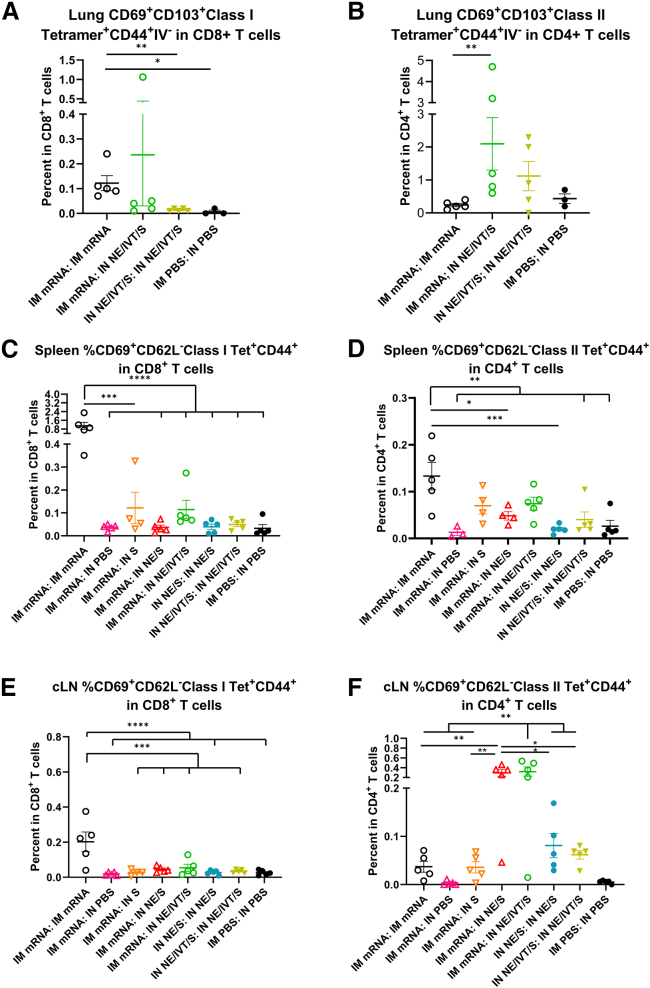
Figure 4.
IM mRNA vaccination is important for generating robust levels of spike-specific CD8+ T cells while IN boosting enhances the frequency of spike-specific CD4+ T cells in the lung and draining LNs
Mice were given 3 μg mRNA IM, 20μg of S protein IN in NE/IVT, or PBS. Cells isolated from the lungs, spleen, and cLNs of mice given prime/boost immunizations with the indicated adjuvant/antigen regimens were incubated with MHC class I (VNFNFNGL) or MHC class II (VTWFHAIHVSGTNGT) tetramers, stained for surface markers, and analyzed by FACS. Frequencies of CD44+IV− Tet+CD69+CD103+ expressing CD8+ (A) or CD4+ (B) TRMs in the lung were quantified. (n = 3–5/group with data represented as mean ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, by Mann-Whitney U test). Frequencies of Tet+CD44+CD69+CD62L− TEMs were similarly quantified in the spleen (C and D) and cLNs (E and F). (n = 3–5/group with data represented as mean ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test shown only for select groups (full statistical analysis is shown in Table S1).