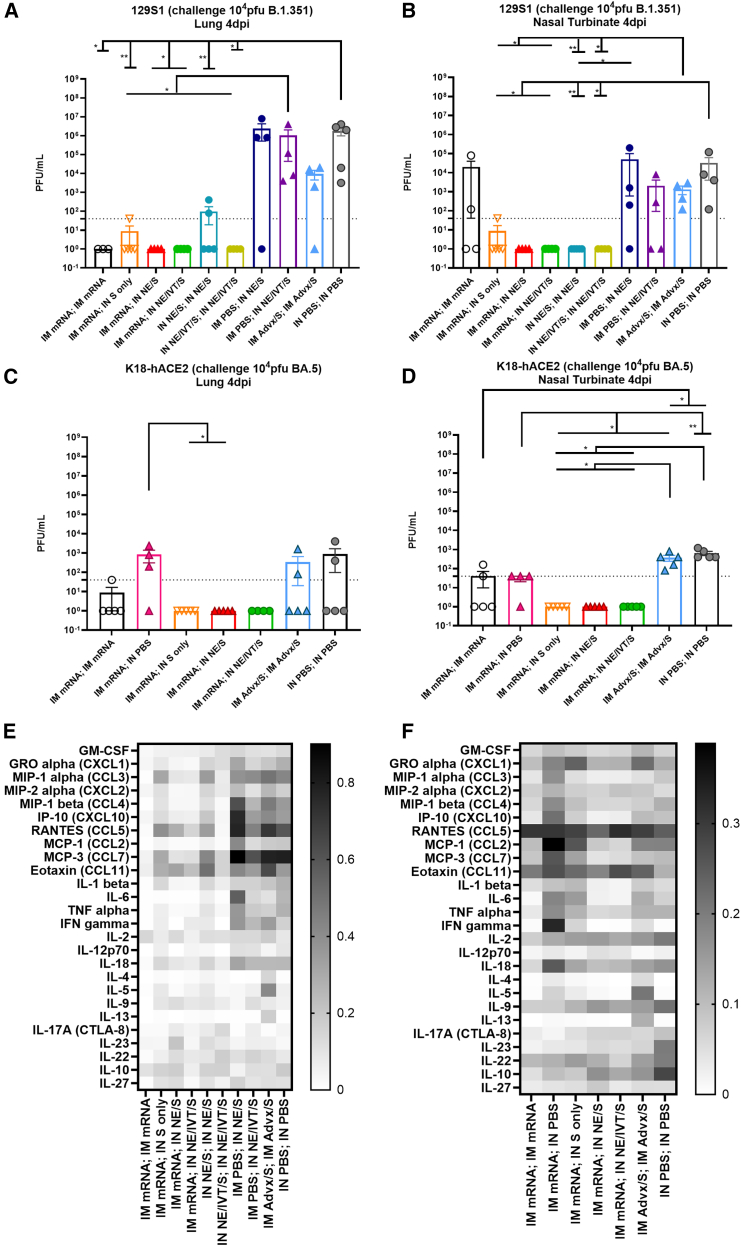
Figure 7.
Heterologous IM/IN prime/pull and IN/IN immunization strategies provide sterilizing immunity upon heterologous challenge in both the upper and lower respiratory tracts in contrast to IM/IM immunization with BNT162b2 mRNA or Addavax/S
129S1 mice were primed either IM with 0.4 μg of mRNA or PBS, or IN with 15 μg S with either NE or NE/IVT. Mice were boosted 4 weeks later IM with 0.4 μg mRNA, or IN with 15 μg S with PBS, NE or NE/IVT as indicated. Groups receiving two immunizations with IM Advx/S or IN PBS were included for comparison. 3 weeks post-boost, mice were challenged IN with 104 PFU B.1.351, and viral titers were measured at 4 d.p.i. in the (A) lungs and (B) nasal turbinates. K18-hACE2 mice were similarly vaccinated and then challenged IN with 104 pfu BA.5. Viral titers were measured at 4 d.p.i. in the (C) lungs and (D) nasal turbinates. Each data point represents the average of replicate counts for each animal (n = 4–5/group; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 by Mann-Whitney U test). Cytokine and chemokine levels in lung homogenate were also measured at 4 d.p.i. by multiplex immunoassay from the immunized (E) 129S1 mice challenged with B.1.351, and the (F) K18-hACE2 mice challenged with BA.5. Individual cytokine/chemokine levels were normalized to the cytokine/chemokine range and then normalized based on multiplication with log2 fold changes to normalize expression changes. Heatmap shows expression changes for the mean of each group. Individual cytokine levels and statistical analyses are provided in Figures S7 and S8.