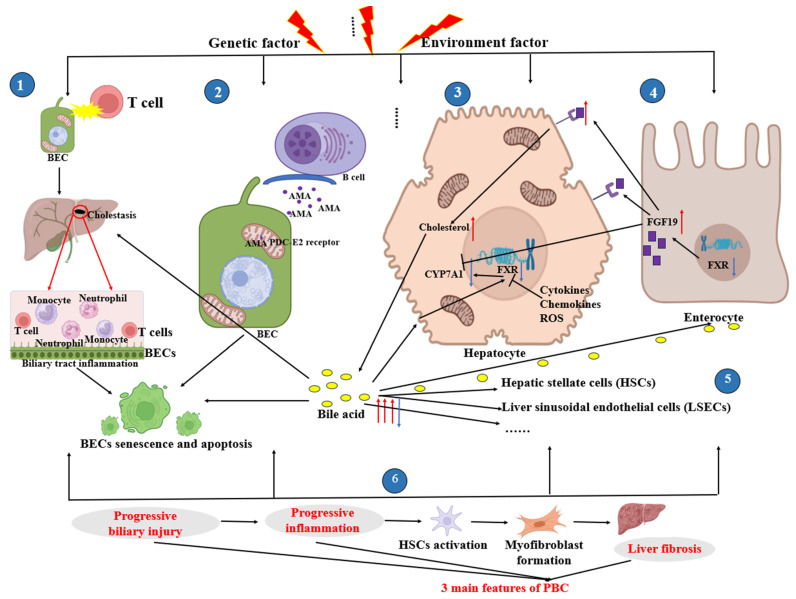
Figure 1.
The fibrotic process of PBC. Diagrams were created with the help of BioRender software (© 2024 BioRender). The diagram displays six processes. ① Against a backdrop of genetic and environmental risk factors for disease, T lymphocytes, which should protect the body from external bacterial and viral attacks, begin to attack the small bile ducts lined by a single layer of BECs in the liver lobules, leading to bile stasis and cholangitis, as well as BEC senescence and apoptosis. ② Plasma cells secrete AMAs, which specifically recognize the PDC-E2 receptor, causing BEC damage and apoptosis. ③ and ④ When hepatocytes are damaged, especially the toxic intermediate and/or inflammatory cytokines, for example, IL-6 regulates FXR via signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation, or reactive oxygen species (ROS) largely affect the expression of FXR, with the reduction of FXR being observed. SHP induced by FXR inhibits the downregulation of CYP7A1 expression, promoting the synthesis of bile acids from cholesterol. After entering the bile ducts, the bile acids are reabsorbed into the intestinal cells via ASBT, activating the intestinal FXR, which increases the expression of FGF19. FGF19 crosses the portal circulation and subsequently binds to its receptor FGFR4/βklotho, promoting the synthesis of bile acids from cholesterol, and the excess bile acids continue to damage the bile ducts. At the same time, the increase in FGF19 may help suppress the expression of CYP7A1. However, during PBC, the expression of CYP7A1 is inhibited, which may be an adaptive response of the body to cholestatic liver injury [51]. ⑤ Bile acids act directly on hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs), and other cells. ⑥ Progressive biliary injury, progressive inflammation, and liver fibrosis are the three main features of PBC. A red arrow indicates an increase, a blue arrow indicates a decrease, and a black arrow indicates an effect on or causes. BECs: biliary epithelial cells; CYP7A1: cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; FXR: farnesoid X receptor; ROS: reactive oxygen species; PBC: primary biliary cholangitis; FGF19: fibroblast growth factor 19; SHP: Small Heterodimer Partner; FGFR4/βklotho: Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4/beta-Klotho.