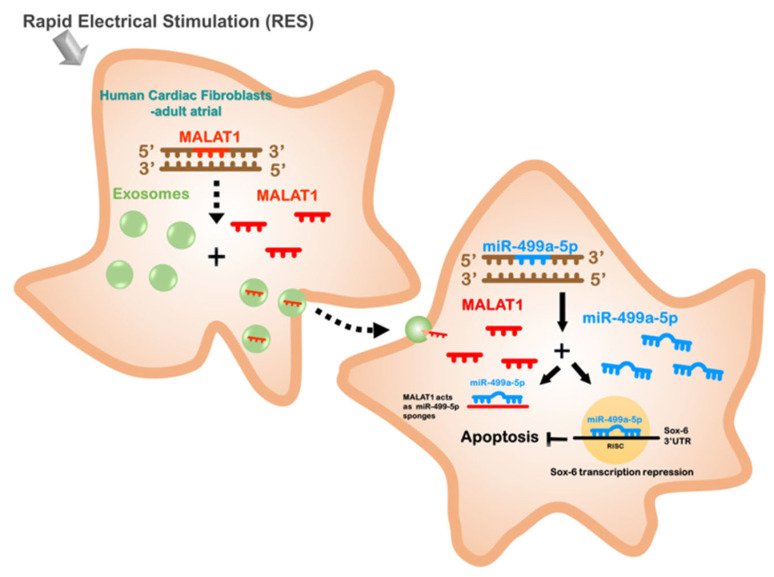
Figure 7.
This schematic illustrates how rapid electrical stimulation (RES) enhances atrial fibrillation through the upregulation of exosomal MALAT1 in human cardiac fibroblasts from adult atria (HCF-aa). Increased exosomal MALAT1 leads to the suppression of miR-499a-5p, resulting in the upregulation of SOX6 expression in HCF-aa. This pathway highlights the critical role of HCF-aa-derived exosomal MALAT1 in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation under RES conditions. Consequently, HCF-aa-derived exosomal MALAT1 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for treating atrial fibrillation.