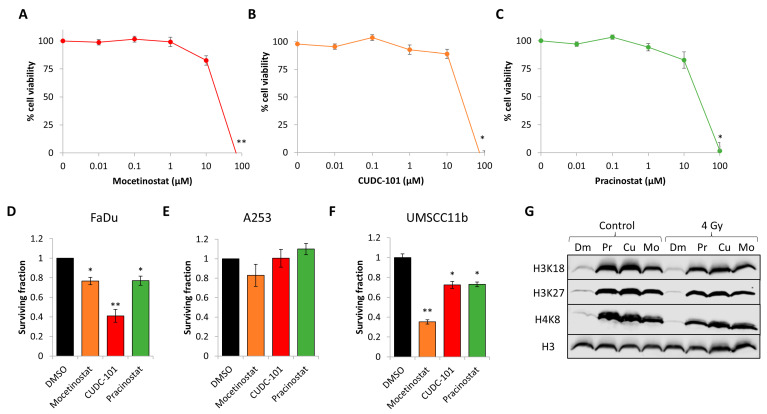
Figure 3.
Effect of mocetinostat, CUDC-101, and pracinostat on HNSCC cell viability, clonogenic survival, and histone acetylation. (A–C) FaDu cells were treated with increasing doses of (A) mocetinostat, (B) CUDC-101, or (C) pracinostat (0.01–100 µM), and cell viability was measured via CellTiter Blue from three biologically independent experiments. Shown is the mean cell viability ± SE. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 on two-sample t-tests compared to the untreated controls. (D) FaDu, (E) A253, and (F) UMSCC11b cells were treated with mocetinostat, CUDC-101, or pracinostat (all 1 µM) in comparison to DMSO as control and clonogenic survival of cells, analysed from three independent experiments. * p < 0.01, ** p < 0.001 on one-sample t-tests compared to the DMSO-treated controls. (G) FaDu cells were treated with DMSO (Dm), 1 µM mocetinostat (Mo), CUDC-101 (Cu), or pracinostat (Pr), and either unirradiated (control) or irradiated with 4 Gy X-rays and cells harvested at 2 h post-irradiation. Histones were purified by acid extraction and analysed by immunoblotting using antibodies targeted against site-specific acetylation sites on histone H3 or H4.