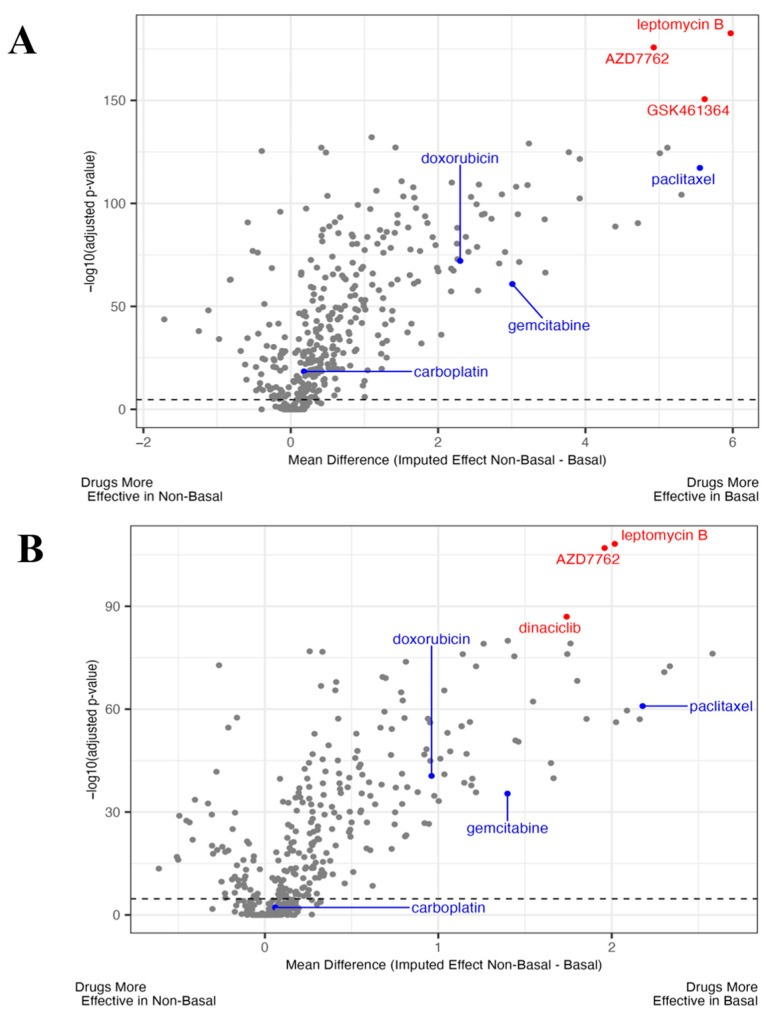
Figure 1.
XPO1 inhibitor was predicted to be more effective in METABRIC and TCGA basal type breast cancer patients. (A) Using our novel virtual drug screening pipeline, we imputed the drug response in the METABRIC breast cancer cohort and stratified patients into TNBC and non-TNBC (i.e., basal or non-basal). Plotted are the t-test results from the comparison of a drug’s predicted effect in TNBC vs. non-TNBC patients, with the effect size shown on the x axis and significance (−log10 of adjusted p -value based on a number of test correction using a Bonferroni adjustment) on the y axis. Dashed black line representing Bonferroni p-value of −log10(0.01). A red dot represents one of the top 3 drugs predicted to be the most efficacious in TNBC patient tumors. The blue dots highlight the current standard-of-care treatment for TNBC patients. The PAM50 status was used due to incomplete IHC status within clinical information. (B) The same analysis as (A) was performed in the independent TCGA clinical breast cancer dataset. In both, leptomycin B, an XPO1 inhibitor is the most significant compound and has one of the largest effect sizes showing higher predicted sensitivity in basal populations.