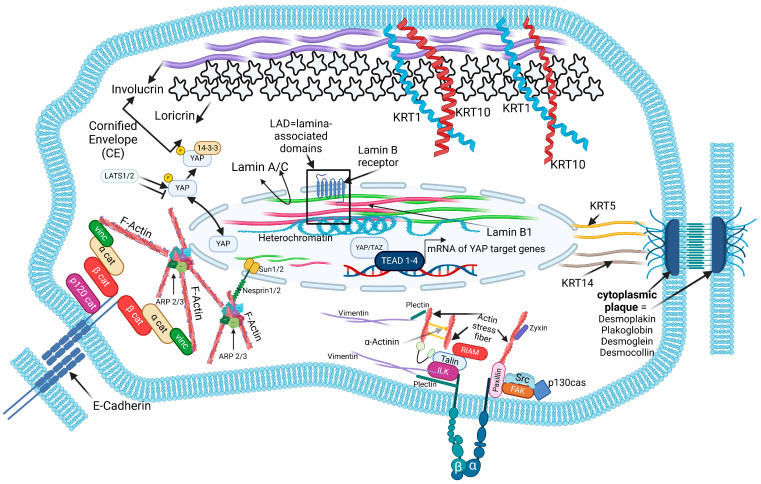
Figure 2.
Model cell that visualizes the biomarkers of interest and their molecular context. In addition to the analyzed cIFs and involucrin (IVL), the following molecules were subject of the investigation: CDH1 (E-cadherin), LOR (loricrin), ITGB1 (integrin β1), ITGB3 (integrin β3), LMNB1 (lamin B1), ACTR2 (actin-related protein 2) and YAP1 (yes-associated protein). CDH1 is a constituent of adherens junctions, which connect neighboring epithelial cells to each other, thereby being indispensable for epithelial morphogenesis [48]. Intracellularly, it binds to the actin filament system via linker proteins of the catenin family [49]. In the context of epithelial keratinocyte differentiation in addition to IVL, LOR is a further marker of terminal differentiation and together with IVL participates in cornified envelope formation. LOR can form crosslinks with itself, thereby yielding different molecular weights [40]. Within the lamina-associated domains, the lamin B receptor tethers heterochromatin via LMNB1 to the inner nuclear membrane [50]. After shuttling to the nucleus, the co-transcriptional activator YAP (and its homologue TAZ, neglected in this study) binds to the TEAD family of transcription factors (TEA Domain Transcription Factor1-4), thereby inducing the expression of YAP target genes [51]. At sites of cell matrix interaction, the cIF VIM is involved in the formation of actin-bound FAs via interaction with the FAs constituent plectin [52,53]. Further constituents of FAs are ITGB1 and ITGB3, whereas ITGB3 appears to play a role in the recruitment of VIM and plectin to FAs [54]. Both of the basal cell-specific keratins, the cIFs KRT5 and KRT14, are connected with DP (Desmoplakin) [55], one of the constituents of the cytoplasmic plaque [56]. At sites of adherens junction-mediated cell-to-cell adhesion, CDH1 is linked to the actin cytoskeleton through members of the catenin family and vinculin (VCL) [57]. At sites of the nuclear envelope, ARP2/3 is involved in the formation of the actin cap, which interacts with the inner part of the nucleus through nesprin 1/2 interaction, the latter connected with the nuclear lamins nIFs via members of the Sun-family proteins Sun 1/2 (Sad1/UNC-84 domain-containing proteins) [58]. Created with BioRender.com.