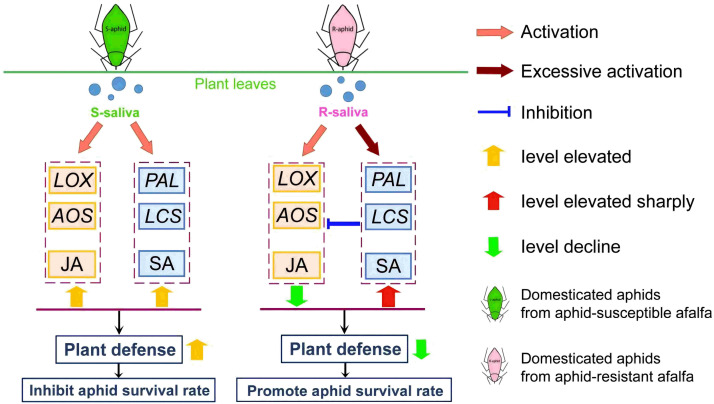
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of changes in gene expression levels related to salicylic acid (SA) plant hormone and jasmonic acid plant hormone (JA) synthesis in host plant leaves after infestation by T. trifolii. When S-aphids infest the leaves of the host plant, the SA plant hormone and JA plant hormone signal pathways of the host plant are activated at the same time; they improve the host plant’s ability to resist the aphids together and then reduce the survival rate of the aphids. However, when R-aphids infested the leaves of the host plant, the SA plant hormone signal pathway is activated excessively, resulting in a sharp increase in SA plant hormone synthesis. The JA plant hormone pathway in the host plant is consequently inhibited, the host plant’s ability to resist aphids is reduced, and the survival rate of the aphids increases.