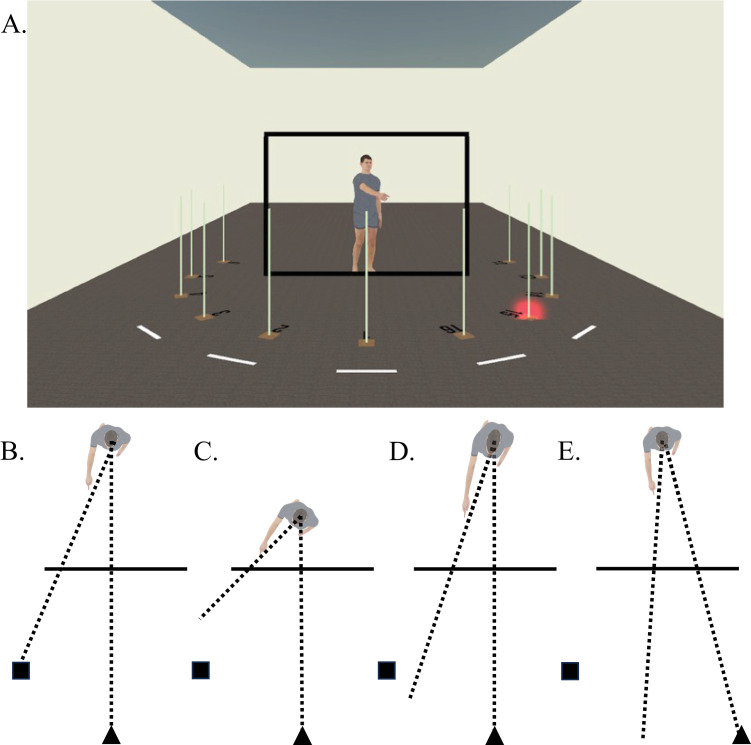
Figure 2.
(A) Illustration of the virtual environment for the exocentric pointing task used in both Wang and Troje (2023) and the present study. (B–E) Illustrations of the exocentric pointing task, where the observer (triangle) adjusts the pointer to a specific target (square). (B) The observer accurately perceives the pointer's distance and his 3D shape in visual space, resulting in the pointer pointing directly at the target. However, if the observer (C) underestimates the pointer's distance, (D) perceives the pointer as expanded in depth, or (E) is at an oblique viewing angle, angular deviations occur between the pointer's pointing direction and the target.