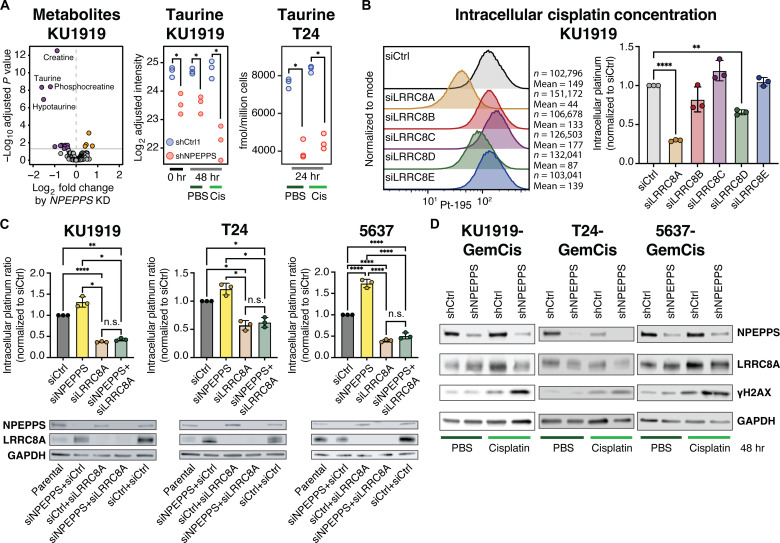
Fig. 2. NPEPPS alters platinum import and DNA damage by modulating VRACs.
(A) Untargeted metabolomics in KU1919 cells with shRNA-mediated NPEPPS suppression or control shRNA. Taurine levels are reported in control (PBS) and cisplatin (Cis) treatment conditions. Targeted metabolomic measured levels of taurine are reported in T24 cells in control (PBS) and cisplatin (Cis) treatment conditions. hr, hours. (B) CyTOF in KU1919 cells shows intracellular cisplatin levels after 4 hours of 10 μM cisplatin with siRNA-mediated suppression of VRAC subunits LRRC8A-E compared to control (scramble) siRNA. Median intracellular cisplatin measurements across biological triplicates were normalized to the siRNA control and compared using a one-way ANOVA (**P < 0.01; ****P < 0.001). (C) Intracellular cisplatin levels for KU1919, T24, and 5637 cells with siRNA-mediated knockdown of NPEPPS alone, LRRC8A alone, or the combination of NPEPPS and LRRC8A knockdown. All samples were normalized to siRNA control samples and compared using a one-way ANOVA (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001). n.s., not significant. Immunoblot validation of the knockdowns is reported with native NPEPPS and LRRC8A antibodies. (D) KU1919, 5637, and T24 cells made resistant to GemCis were treated with cisplatin (10 μM) or PBS for 48 hours. Immunoblots with NPEPPS, LRRC8A, and phospho-γ-H2AX antibodies are shown, comparing shRNA-mediated knockdown of NPEPPS to shRNA scramble controls.