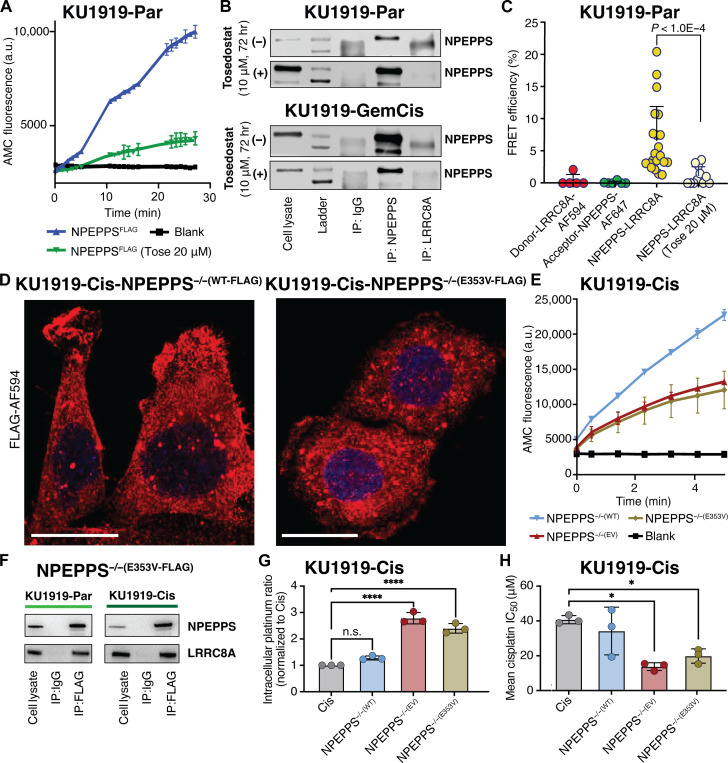
Fig. 4. NPEPPS enzymatic function is critical for the NPEPPS-LRRC8A interaction.
(A) Quantification of NPEPPS enzymatic activity on the H-Leu-AMC substrate with vehicle (PBS, 0 μM) or tosedostat (20 μM) treatment in NPEPPSFLAG KU1919 parental cells. a.u., arbitrary units. (B) Immunoblot of NPEPPS and LRRC8A in KU1919 parental and GemCis-resistant cells after IP with native NPEPPS or LRRCA antibodies following 72 hours of PBS control (0 μM) or tosedostat (10 μM) treatment. (C) Quantification of NPEPPS-LRRC8A colocalization by FRET-AB in LRRC8AFLAG KU1919 parental cells with vehicle (PBS, 0 μM) or tosedostat (20 μM) treatment. The relative quantification is reported as FRET efficiency (%) and statistical comparisons were made using the Mann-Whitney U test. (D) Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy of NPEPPSFLAG constructs [NPEPPS−/−(WT-FLAG) and NPEPPS−/−(E353V-FLAG)] in cisplatin-resistant KU1919 cells. Scale bars, 20 μm. (E) Quantification of NPEPPS enzymatic activity on the H-Leu-AMC substrate in KU1919-Cis cells expressing NPEPPS−/−(WT-FLAG) or NPEPPS−/−(E353V-FLAG). (F) Immunoblots of NPEPPS and LRRC8A following anti-FLAG IP in parental and cisplatin-resistant KU1919 cells expressing NPEPPS−/−(WT-FLAG) or NPEPPS−/−(E353V-FLAG). (G) Intracellular cisplatin concentrations were measured by CyTOF in triplicate experiments in WT KU1919-Cis cells or KU1919-Cis cells expressing NPEPPS−/−(WT-FLAG) or NPEPPS−/−(E353V-FLAG). Cisplatin concentrations were normalized to the unmodified cisplatin-resistant KU1919 cells, and comparisons were made using one-way ANOVA (****P < 0.0001). (H) Cisplatin IC50 was measured in technical and biological triplicate by IncuCyte Zoom analysis over 120 hours of treatment in WT KU1919-Cis cells or KU1919-Cis cells expressing NPEPPS−/−(WT-FLAG) or NPEPPS−/−(E353V-FLAG). Results are reported as the mean IC50 ± SD. Comparisons were made using one-way ANOVA (*P < 0.05).