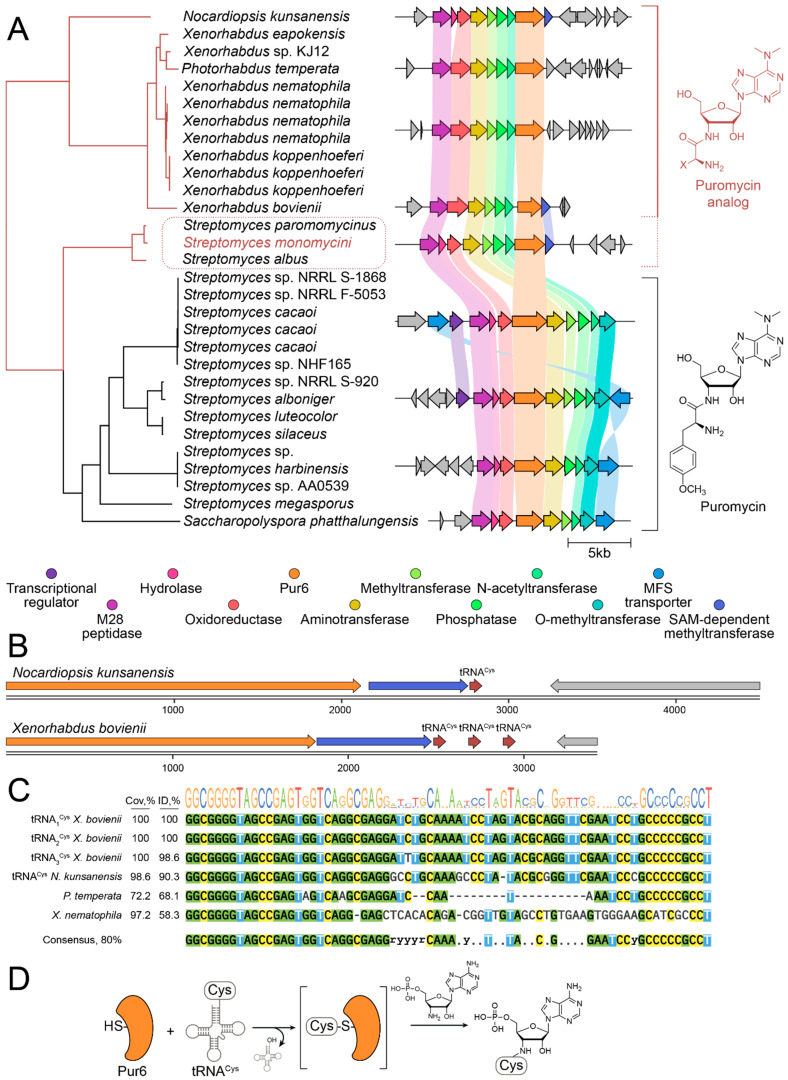
Figure 2.
Pur6-guided genome mining revealed the biodiversity of puromycin analogs in Streptomyces and Xenorhabdus. (A) Pur6 and its homologs are strongly associated with BGC of puromycin-like secondary metabolites. The phylogenetic tree indicates the distance between Pur6 homologs in various bacteria. The corresponding genomic context and puromycin BGCs are colored with grey and rainbow, respectively. Putative BGCs associated with puromycin biosynthesis and biosynthesis of puromycin-like analogs are united by brackets and colored with black and red, respectively. Putative new analogs of puromycin in streptomycetes are highlighted with a red dotted line. (B) BGCs of puromycin-like secondary metabolites in Nocardiopsis kunsanensis and Xenorhabdus bovienii have cysteine tRNA. (C) Sequences of tRNACys and similar RNA sequences encoded in the genomic context of BGCs of puromycin-like secondary metabolites. (D) Putative reaction scheme illustrating a potential working principle of Pur6-like enzymes.