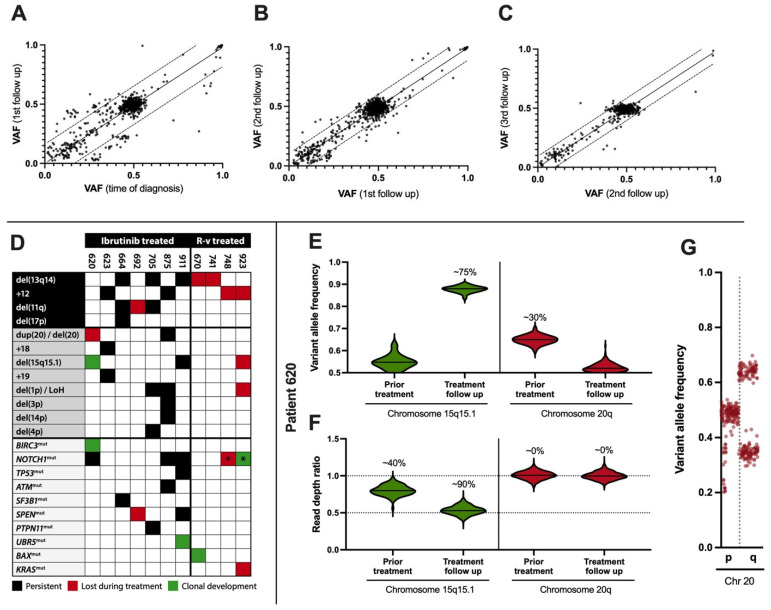
Figure 2.
Genomic stability following ibrutinib treatment. Correlation between somatic variants in CD19+ cells prior to treatment and at first follow-up ((A), ρPearson = 0.86, slope 0.98, pt-statistics < 10−4, mean follow-up 11 months, n = 7), between first and second follow-up ((B), ρ = 0.95, slope 0.99, p < 10−4, 20 months, n = 7), and between second and third follow-up ((C), ρ = 0.94, slope 0.98, p < 10−4, 34 months, n = 5). Cytogenetic markers del(13q14) and trisomy 12 following rituximab–venetoclax (R–v) treatment and copy-number alterations (CNAs) for ibrutinib-treated patients (D). NOTCH1 frameshift mutation c.7541–7542del (p.P2514Rfs*4, COSV53024776, GRCh38, 9:136496197 CAG>C) was detected with a variant allele frequency of 0.21 in R–v patient 923 at first follow-up (marked *). The same mutation was detected with a variant allele frequency decreasing to 0.03 in R–v patient 748 (*). Allelic imbalances and CNAs on chromosome 15q and 20q, including the BIRC3 mutation, were found for patient 620. The clonal burden of chromosome 15q deletion increased from less than 50% to more than 50% during treatment (E,F) and copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity at 20q during follow-up (solid lines separate chromosome 15q and 20q, dotted lines denote the theoretical ratios for disomy, 1.0, and deletion, 0.5). Allelic imbalance on chromosome 20 was evaluated at 30% burden ((G), a dotted line separates chromosomal p and q arm).