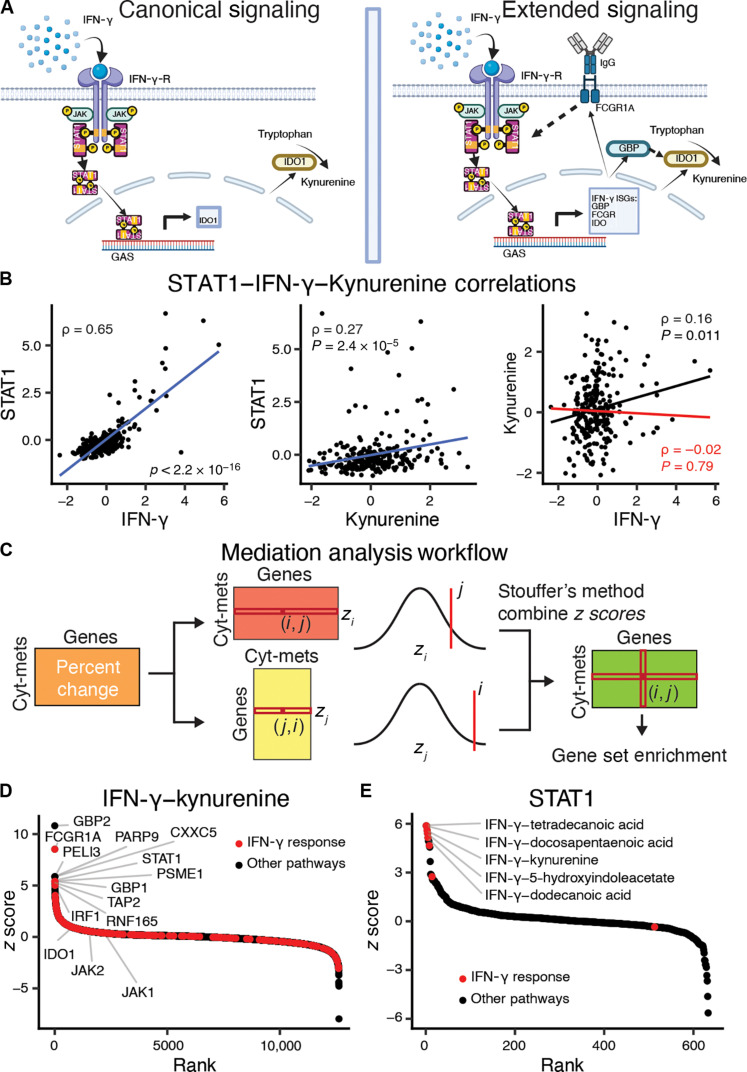
Fig. 2. Cytokines induce gene expression changes that mediate metabolite levels.
(A) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) is the rate-limiting enzyme in the conversion of tryptophan to kynurenine and is induced by IFN-γ signaling. IFN-γ signals through the IFN-γ receptor activating STAT1, which then up-regulates IDO1 via binding to the gamma interferon activation site (GAS). The right panel extends this signaling pathway based on the mediation analysis to include other ISGs. Created using BioRender.com. (B) Scatterplots for IFN-γ–STAT1, kynurenine-STAT1, and IFN-γ–kynurenine. Blue lines represent the lines of best fit between the features. The red line represents the linear fits of the partial correlation coefficient after adjustment for STAT1 expression. Spearman direct correlation (black) and partial correlation (red) statistics are reported. (C) Overview of the mediation analysis algorithm to identify immunometabolic relationships that are conditioned on gene expression. The partial Spearman correlation coefficients between cytokines and metabolites after adjusting for transcript abundances is compared to the direct Spearman correlations between cytokines and metabolites. The percentage changes between the partial and direct correlations over all cytokine-metabolite relationships and gene transcripts are calculated, and then both the cytokine-metabolite and gene axes are z-score normalized. Last, the z scores are combined using Stouffer’s method to combine z scores. (D) Gene mediation rankings for IFN-γ–kynurenine with IFN-γ response genes highlighted in red. (E) Cytokine-metabolite rankings for mediation by STAT1 with cytokine-metabolite relationships enriched for IFN-γ response genes are highlighted in red. FCGR, Fcγ receptor; GBP, guanylate-binding protein; IgG, immunoglobulin G; JAK, Janus kinase; PARP9, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase.