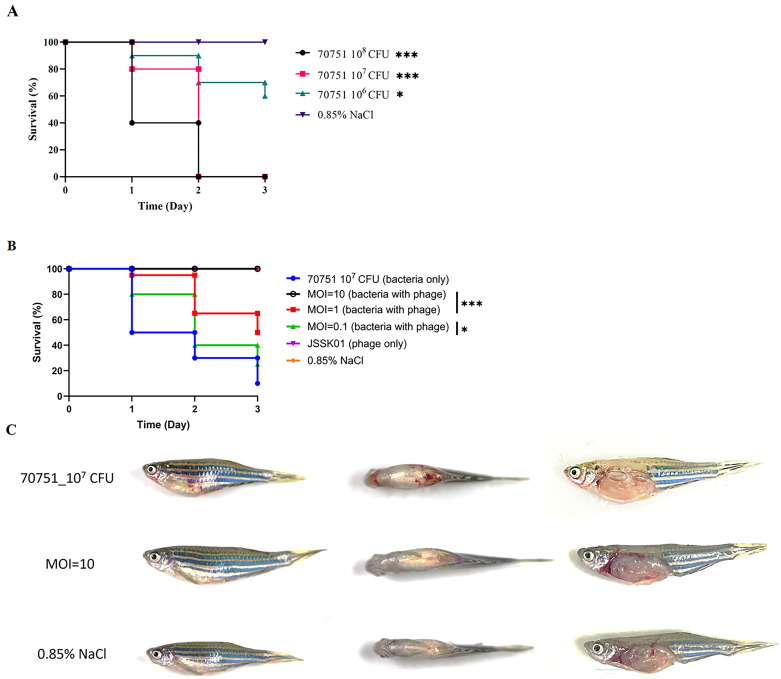
Figure 5.
JSSK01 can rescue MDR 70751-infected zebrafish. (A) A lethal dose assessment was conducted on three groups of adult zebrafish, each comprising 10 fish. These groups were subjected to intraperitoneal injections of MDR 70751 at various concentrations (108, 107, and 106 CFU in 20 µL of media, as well as 0.85% NaCl as the negative control, represented by the black, red, green, and purple lines, respectively). (B) Zebrafish were subjected to JSSK01 treatment (MOI = 10, 1, 0.1) for 30 min after bacterial infection with 107 CFU (black line, red line, green line). Additionally, a group received JSSK01 treatment alone (2.5 × 107 CFU/20 µL, purple line), whereas a negative control group received 0.85% NaCl (orange line). (C) The manifestation of disease symptoms in zebrafish infected with E. coli 70751 alone was compared with that in the groups rescued by the phage (MOI = 10) and the control group (0.85% NaCl). The views provided are as follows: left, side view; middle, top view; and right, abdominal anatomy. Kaplan–Meier Survival curves were plotted, with the X-axis denoting days post-infection and the Y-axis indicating the survival percentage. Statistical analysis was conducted via log-rank and generalized Wilcoxon tests in GraphPad Prism 9 software, where *** and * indicate p < 0.001 and p < 0.05, respectively.