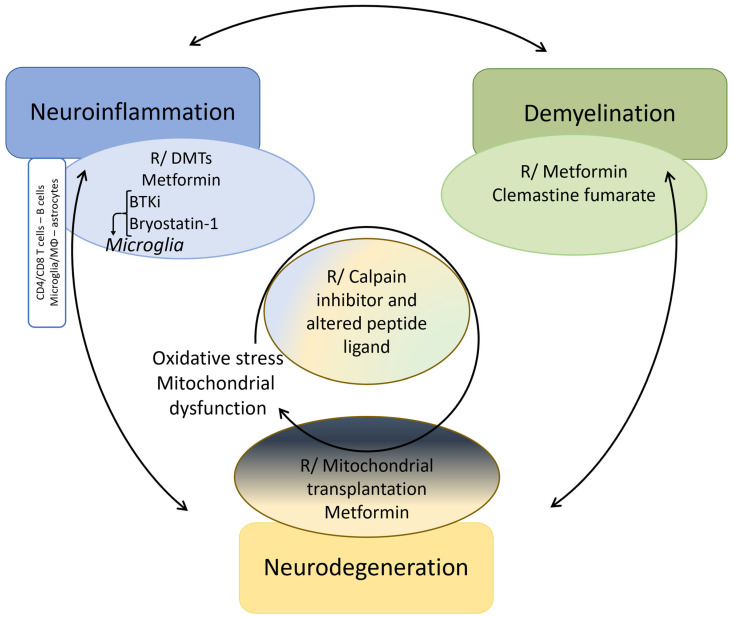
Figure 7.
A few novel therapeutic strategies in MS. The well-known DMTs act mainly on the peripheral adaptive immune system by their immunomodulatory properties or by selectively depleting lymphocytes or by impeding their migration. BTK inhibitors and Bryostatin-1 finally add microglia to the panel of therapeutic targets. BTK inhibitors target B cells but could also offer additional benefits by modulating macrophages and microglia. Bryostatin-1 programs microglia/macrophages toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Clemastine fumarate promotes OPC differentiation. Metformin has anti-inflammatory properties by reducing microgliosis/astrogliosis and proinflammatory mediators, it reduces oxidative stress, rejuvenizes OPCs, and may enhance neurogenesis. In a yet experimental combination therapy, a calpain inhibitor acts within the 3 facets by reducing myelin loss, axonal damage, and CD4+ T cell expansion, while an altered peptide ligand of MBP alters the effector function of T cells. Finally, mitochondrial transplantation could enhance the number of functional mitochondria in all cell types but would in particular be effective in neurons. BTKi = Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, DMT = disease-modifying therapies, MΦ = macrophages, R/ = treatment.