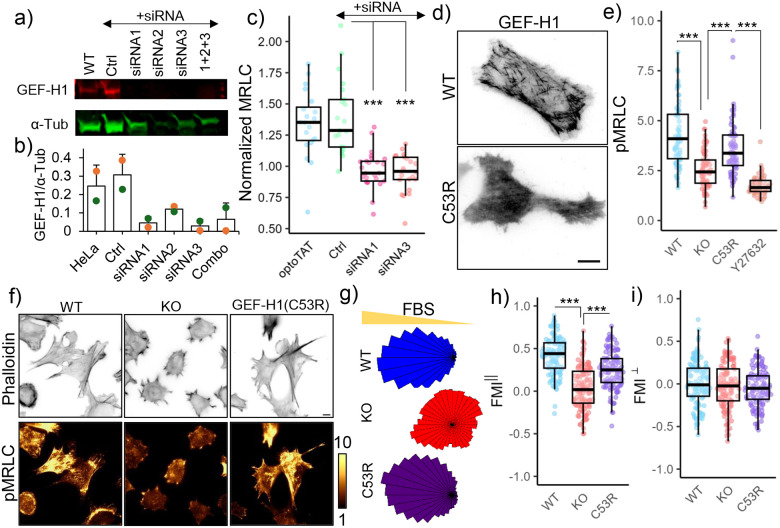
Figure 6. GEF-H1 mediates microtubule acetylation dependent actomyosin contractility.
a), b) GEF-H1 knock-down in HeLa cells by siRNA; c) Changes in mCherry-MRLC intensity on miRFP703-optoTAT stimulation in HeLa cells with optoTAT (20 cells), scramble siRNA (21 cells), siRNA1 (25 cells) and siRNA3 (22 cells) against GEF-H1; d) TIRF images of HeLa cells expressing GFP-GEF-H1 (top panel) and mCherry-GEF-H1(C53R); e) Phospho-MRLC levels in WT (67 cells), α-TAT1 KO (69 cells), α-TAT1 KO MEFs expressing mCherry-GEF-H1(C53R) (67 cells) and same cells treated with 10 μM Y-27632 (60 cells); f) Phalloidin and phospho-MRLC distribution in WT, α-TAT1 KO MEFs and α-TAT1 KO MEFs expressing mCherry-GEF-H1(C53R); g) Rose plots of WT, α-TAT1 KO and KO-GEF-H1(C53R) MEFs migrating in a chemotactic gradient; g) Forward migration indices along the chemotactic gradient and h) Forward migration indices perpendicular to the chemotactic gradient for WT, α-TAT1 KO and KO-GEF-H1(C53R) MEFs, n = 120 cells (40 each from three independent experiments). Scale bar: 10 μm. ***: p<0.001