Abstract
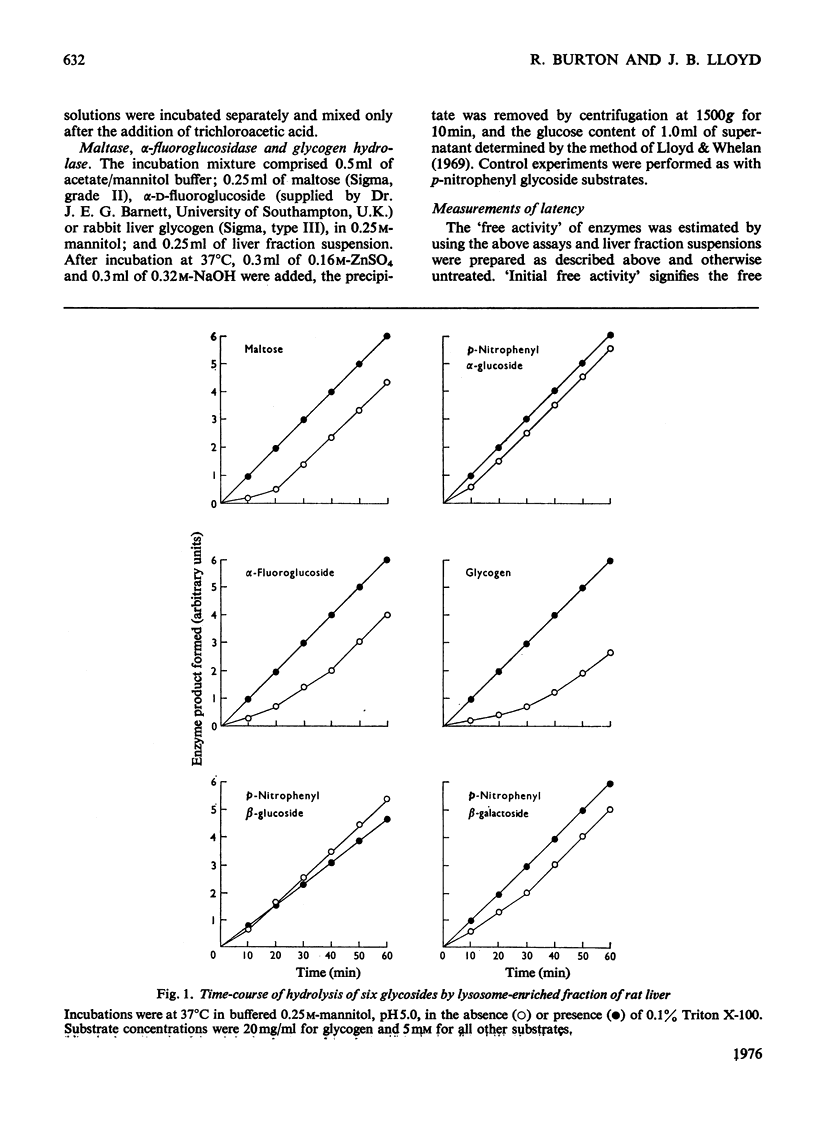
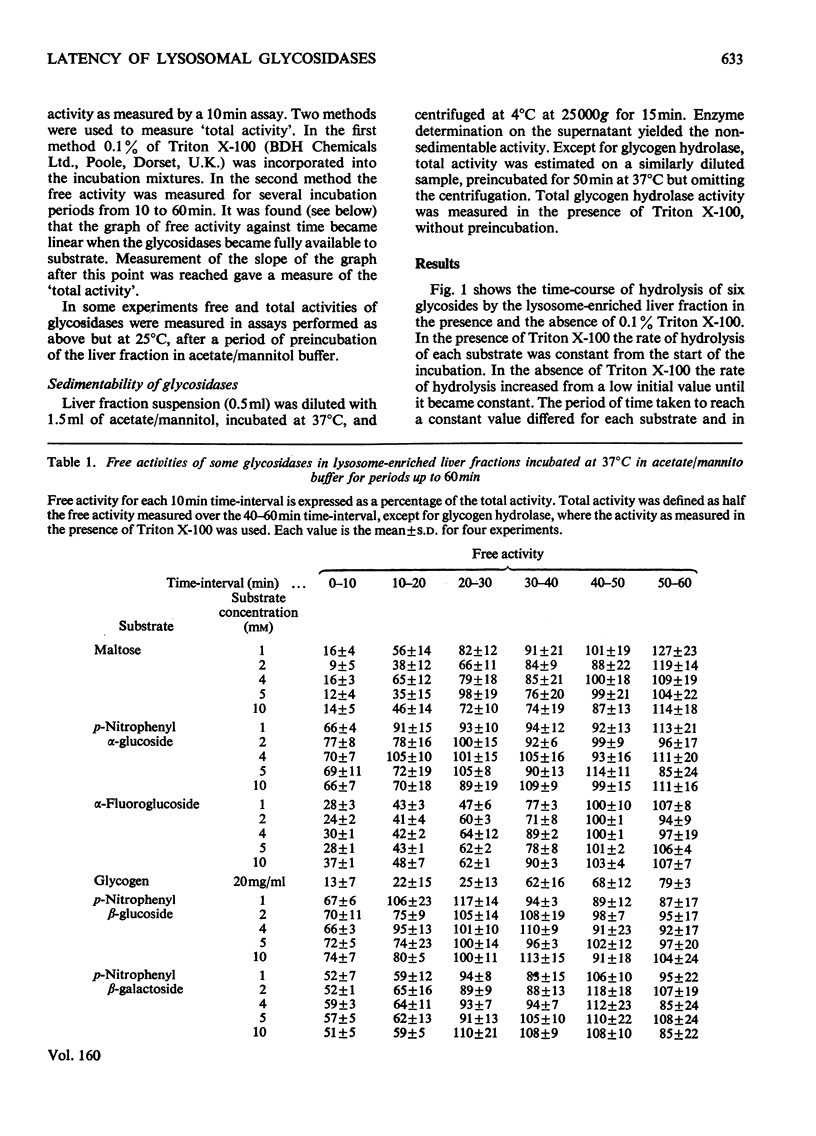
The latency of the alpha-glucosidase activity of intact rat liver lysosomes was studied by using four substrates (glycogen, maltose, p-nitrophenyl, alpha-glucoside, alpha-fluoroglucoside) at a range of substrate concentrations. The results indicate that the entire lysosome population is impermeable to glycogen and maltose, but a proportion of lysosomes are permeable to alpha-fluoroglucoside and a still higher proportion permeable to p-nitrophenyl alpha-glucoside. Incubation at 37 degrees C in an osmotically protected buffer of of pH 5.0 caused lysosomes to become permeable to previously impermeant substrates and ultimately to release their alpha-glucosidase into the medium. The latencies of lysosomal beta-glucosidase and beta-galactosidase were examined by using p-nitrophenyl beta-glucoside and beta-galactoside as substrates. The results indicate permeability properties to these substrates similar to that to p-nitrophenyl alpha-glucoside. On incubation in an osmotically protected buffer of pH 5, lysosomes progressively released their beta-galactosidase in soluble form, but beta-glucosidase remained attached to sedimentable material. Lysosomal beta-glucosidase was inhibited by 0.1% Triton X-100; alpha-glucosidase and beta-galactosidase were not inhibited.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baccino F. M., Zuretti M. F. Structural equivalents of latency for lysosome hydrolases. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):97–108. doi: 10.1042/bj1460097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett J. E., Jarvis W. T., Munday K. A. Enzymic hydrolysis of the carbon-fluorine bond of alpha-D-glucosyl fluoride by rat intestinal mucosa. Localization of intestinal maltase. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):699–704. doi: 10.1042/bj1030699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett J. E., Jarvis W. T., Munday K. A. The hydrolysis of glycosyl fluorides by glycosidases. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):669–672. doi: 10.1042/bj1050669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C., Tappel A. L. Rat-liver lysosomal beta-glucosidase: a membrane enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 8;151(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. I., Brown D. H., Jeffrey P. L. Simultaneous absence of alpha-1,4-glucosidase and alpha-1,6-glucosidase activities (pH 4) in tissues of children with type II glycogen storage disease. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1423–1428. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton R. R., MacKenzie W. F. Heart pathology associated with exposure to high sustained +Gz. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1975 Oct;46(10):1251–1253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A., Ehrenreich B. A. The uptake, storage, and intracellular hydrolysis of carbohydrates by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):201–225. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., WATTIAUX R. Tissue fractionation studies. VII. Release of bound hydrolases by means of triton X-100. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):606–608. doi: 10.1042/bj0630606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C. The separation and characterization of subcellular particles. Harvey Lect. 1965;59:49–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluharty A. L., Scott M. L., Porter M. T., Kihara H., Wilson M. G., Towner J. W. Acid -glucosidase in amniotic fluid. Biochem Med. 1973 Feb;7(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(73)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth A. J., Robinson D. Specificity and multiple forms of beta-galactosidase in the rat. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):59–66. doi: 10.1042/bj0970059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. L., Brown D. H., Brown B. I. Studies of lysosomal alpha-glucosidase. I. Purification and properties of the rat liver enzyme. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1403–1415. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. L., Brown D. H., Brown B. I. Studies of lysosomal alpha-glucosidase. II. Kinetics of action of the rat liver enzyme. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1416–1422. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. B. A study of permeability of lysosomes to amino acids and small peptides. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):245–248. doi: 10.1042/bj1210245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. B. Studies on the permeability of rat liver lysosomes to carbohydrates. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):703–707. doi: 10.1042/bj1150703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer T. N. The maltase, glucoamylase and transglucosylase activities of acid -glucosidase from rabbit muscle. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):713–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1240713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Abrahams H. E. Beta-D-xylosidase in pig kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jan 11;132(1):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld E. L., Belenki D. M. La dégradation du glycogène et du maltose a l'aide de la gamma-amylase de foie de lapin en présence de sucres divers et de leurs dérivés. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968 Nov 5;50(7):1305–1312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salafsky I. S., Nadler H. L. A fluorometric assay of alpha-glucosidase and its application in the study of Pompe's disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Mar;81(3):450–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


